概述
在正式开始之前,我们需要先了解以下几个概念:
-
CLI(Common Language Infrastructure,通用语言框架):提供了一套可执行代码和它所运行需要的虚拟执行环境的规范.
-
CLR(Common Language Runtime,公共语言运行时):和Java虚拟机一样也是一个运行时环境,负责资源管理(内存分配和垃圾收集),并保证应用和底层操作系统之间必要的分离.可以说微软的.NET基础CLR是CLI的一个实例.
-
C++ /CLI:实现了C和.NET的无缝连接,可以使用C和C#混合的方式来完成应用程序代码的编写.
-
.NET程序编译运行流程:将源代码编译为微软中间语言MSIL,运行的时候即时编译为本地机器语言,同时.NET代码运行时有一个CLR环境来管理程序.
对于Hook来说,首先关键的一步就是确定目标函数的地址,而.NET程序的Native函数地址是运行的时候即时编译的,函数地址不确定.但幸运的是我们可以通过C#的RuntimeMethodHandle.GetFunctionPointer()函数来获取编译后的Native函数地址,另外需要注意一点的就是在.NET中,假设函数没有被直接或间接使用,那函数就不会被编译.因此在使用上述接口获取编译后的Native函数地址之前,我们还需要使用C#中的System::Runtime::CompilerServices::RuntimeHelpers::PrepareMethod()函数来进行函数的编译.
通过上述描述,我们可以很轻易就想到用C++来完成Hook代码的编写,用C#来完成.NET程序函数编译地址的确定.
目标程序
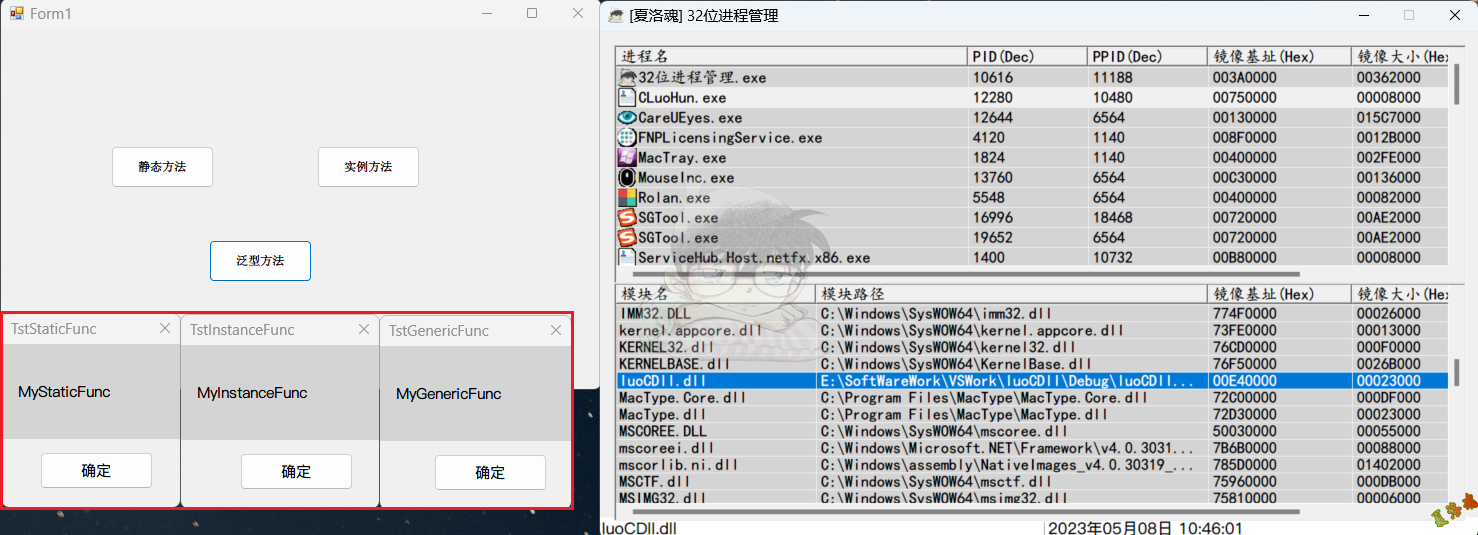
假设我们要Hook的目标C#窗体应用程序如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CLuoHun
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnStatic_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
TstStaticFunc("TstStaticFunc");
}
private void btnInstance_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
TstInstanceFunc("TstInstanceFunc");
}
private void btnGeneric_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
TstGenericFunc("TstGenericFunc");
}
//静态方法
public static void TstStaticFunc(String strMsg)
{
MessageBox.Show(strMsg);
}
//实例方法
private void TstInstanceFunc(String strMsg)
{
MessageBox.Show(strMsg);
}
//泛型方法
private void TstGenericFunc<T>(T strMsg)
{
MessageBox.Show(strMsg.ToString());
}
}
}
|
后面我们以静态方法TstStaticFunc、实例方法TstInstanceFunc以及泛型方法TstGenericFunc为例来展开讲解C++ /CLI Hook代码的编写.
Hook代码
- 创建一个C++ Dll项目,启用CLR支持

- 修改编译选项

在配置属性下C/C++的命令行中添加/Zc:twoPhase-
- Dll的Hook代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
|
#using <mscorlib.dll>
#include <msclr\marshal_cppstd.h>
using namespace System;
using namespace std;
using namespace Reflection;
using namespace System::Runtime::InteropServices;
using namespace msclr::interop;
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include "Detours/include/LuoDetours.h"
#include "OutputDebugString/OutDebuf.h"
void __clrcall MyStaticFunc(String^ strMsg)
{
//cli的string转c++ char*
char* szMsg = (char*)(void*)Marshal::StringToHGlobalAnsi(strMsg).ToPointer();
MessageBoxA(NULL, "MyStaticFunc", szMsg, MB_OK);
}
void __clrcall MyInstanceFunc(Object% obj, String^ strMsg)
{
//cli的string转c++ char*
char* szMsg = (char*)(void*)Marshal::StringToHGlobalAnsi(strMsg).ToPointer();
MessageBoxA(NULL, "MyInstanceFunc", szMsg, MB_OK);
}
void __clrcall MyGenericFunc(Object% obj, String^ strMsg)
{
//cli的string转c++ char*
char* szMsg = (char*)(void*)Marshal::StringToHGlobalAnsi(strMsg).ToPointer();
MessageBoxA(NULL, "MyGenericFunc", szMsg, MB_OK);
}
DWORD WINAPI ThreadProc(LPVOID lpThreadParameter)
{
//①反射找到函数
Type^ type = Type::GetType("CLuoHun.Form1, CLuoHun");
//静态方法 public static void TstStaticFunc(String strMsg)
MethodInfo^ staticMethod = type->GetMethod("TstStaticFunc", BindingFlags::Public | BindingFlags::Static);
//实例方法 private void TstInstanceFunc(String strMsg)
MethodInfo^ instanceMethod = type->GetMethod("TstInstanceFunc", BindingFlags::NonPublic | BindingFlags::Instance);
//泛型方法 private void TstGenericFunc<T>(T strMsg)
MethodInfo^ genericMethodPre = type->GetMethod("TstGenericFunc", BindingFlags::NonPublic | BindingFlags::Instance);
MethodInfo^ genericMethod = genericMethodPre->MakeGenericMethod(String::typeid);
//②JIT 编译函数
System::Runtime::CompilerServices::RuntimeHelpers::PrepareMethod(staticMethod->MethodHandle);
System::Runtime::CompilerServices::RuntimeHelpers::PrepareMethod(instanceMethod->MethodHandle);
System::Runtime::CompilerServices::RuntimeHelpers::PrepareMethod(genericMethod->MethodHandle);
//③获取函数地址
void* staticMethodAddr = (void*)staticMethod->MethodHandle.GetFunctionPointer();
void* instanceMethodAddr = (void*)instanceMethod->MethodHandle.GetFunctionPointer();
void* genericMethodAddr = (void*)genericMethod->MethodHandle.GetFunctionPointer();
//DbgPrintf("TstStaticFunc address: 0x%x", staticMethodAddr);
//DbgPrintf("TstInstanceFunc address: 0x%x", instanceMethodAddr);
//DbgPrintf("TstGenericFunc address: 0x%x", genericMethodAddr);
//④Hook
AddHook(&(PVOID&)staticMethodAddr, MyStaticFunc);
AddHook(&(PVOID&)instanceMethodAddr, MyInstanceFunc);
AddHook(&(PVOID&)genericMethodAddr, MyGenericFunc);
return TRUE;
}
//#pragma unmanaged
#pragma managed(push, off) //编译为native代码
BOOL APIENTRY DllMain( HMODULE hModule,
DWORD dwReason,
LPVOID lpReserved
)
{
if (dwReason == DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH)
{
DisableThreadLibraryCalls(hModule);
::CreateThread(NULL, NULL, ThreadProc, NULL, NULL, NULL);
}
else if (dwReason == DLL_PROCESS_DETACH)
{
}
return TRUE;
}
#pragma managed(pop)
|
注意
-
对于Dll工程来说,需要使用pragma指令将DllMain函数编译为native代码
-
Hook函数的调用约定为__clrcall
-
对于实例函数的Hook,要多写一个Object参数
-
对于泛型方法,要调用MethodInfo.MakeGenericMethod函数为其提供具体的类型参数
- 将上述代码编写的Dll注入到目标C#程序中即可实现指定函数的Hook
总结
对.NET程序的Hook,当然也可以通过C#这种高级语言来完成,但是异常麻烦.C++ /CLI通过将托管环境和Native环境整合在一起,允许开发者在编写托管代码的同时,仍能直接访问Native代码,借助于C++操作底层代码的强大特性,我们可以很轻易的完成Hook操作.
参考链接
C++/CLI
托管C++、C++/CLI、CLR
managed 和 unmanaged pragma
C++/CLI实现inline hook .NET程序
AMSI 绕过之.Net API Hook


