除法
约定
- 两个无符号相除,结果仍然是无符号.
- 两个有符号相除,结果是有符号.
- 有符号数和无符号数混除,结果是无符号的.
基本概念
在C语言和其他多数高级语言中,对整数除法规定为向零取整.
- 向下取整
取得往负无穷方向接近x的整数值.
向下取整的除法,当除数为2的幂时,可以直接用带符号右移指令(sar)来完成.
但是,向下取整存在一个问题:
$$
⌊\frac{-a}{b}⌋ \not= -⌊\frac{a}{b}⌋ (假设\frac{a}{b}结果不为整数)
$$
- 向上取整
取得往正无穷方向接近x的整数值.
向上取整也存在一个问题:
$$
⌈\frac{-a}{b}⌉ \not= -⌈\frac{a}{b}⌉ (假设\frac{a}{b}结果不为整数)
$$
- 向零取整
取得往0方向最接近x的整数值.
向零取整的除法满足:
$$
[\frac{-a}{b}] = [\frac{a}{-b}] =-[\frac{a}{b}]
$$
无符号除法
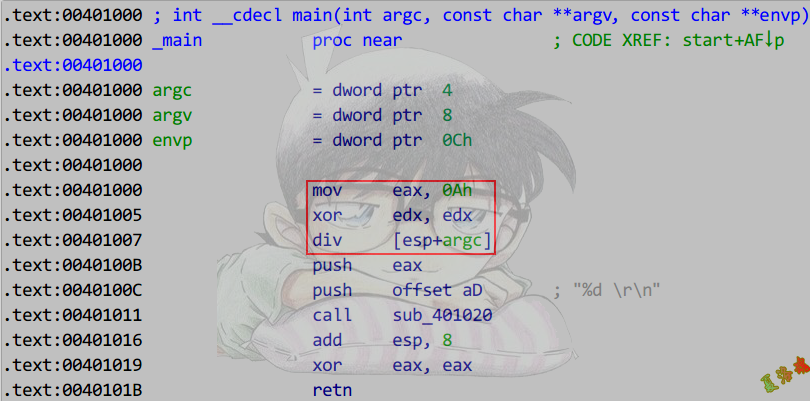
除数为变量
除数为变量的时候是没有优化,只能使用除法指令,这里的变量是指类似argc这类在编译期间不能计算的变量.
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(unsigned int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d \r\n", 10 / argc);
return 0;
}
|
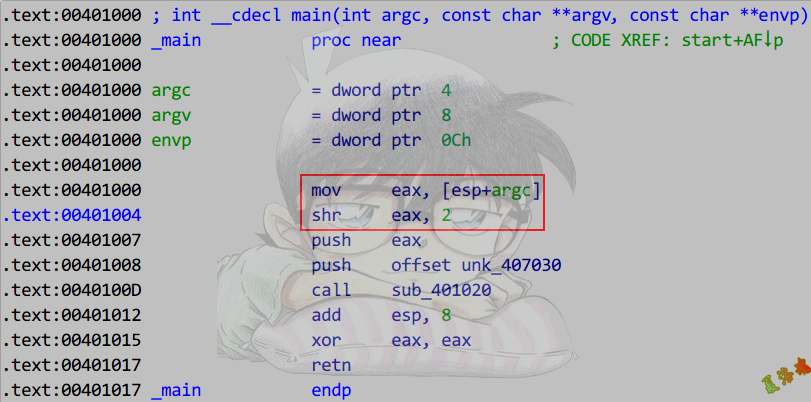
除数为2的幂
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(unsigned int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d", argc / 4);
return 0;
}
|
除数为非2的幂
MagicNumber无进位
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(unsigned int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d \r\n", argc / 3);
return 0;
}
|
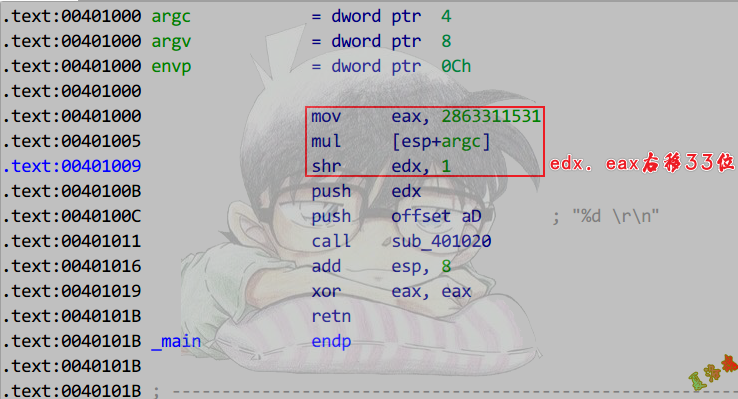
推导

特征
1
2
3
|
mov eax, MagicNumber
mul 被除数
shr edx, n ;这条指令可无
|
还原
1
2
|
除数 = 2^(32 + n) / MagicNumber
结果向上取整
|
MagicNumber有进位
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(unsigned int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d", argc / 7);
return 0;
}
|
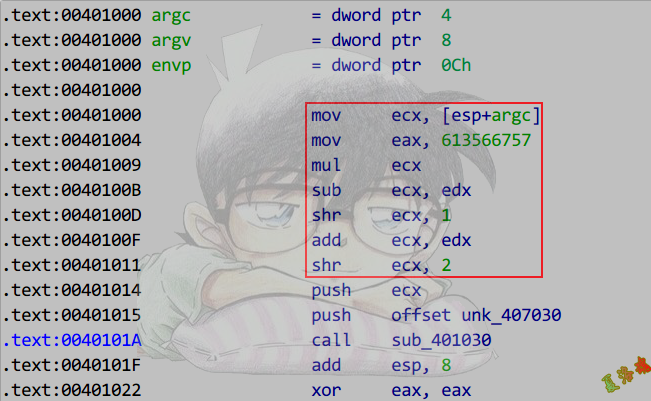
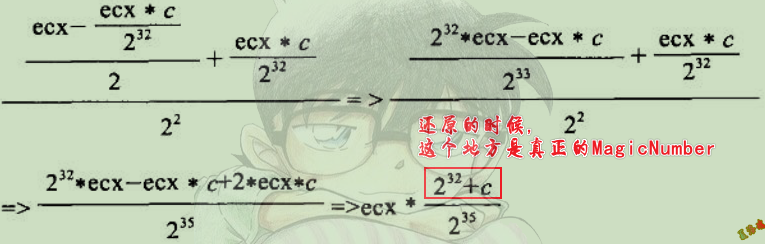
推导

特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
#乘减移加移
mov reg, 被除数
mov eax, MagicNumber
mul reg
sub reg, edx
shr reg, 1
add reg, edx
shr reg, A; 这句可能没有
;此后直接使用reg的值, eax弃而不用
|
还原
1
2
3
|
统计右移次数,n = 32 + 1 + A
除数 = 2^n / (2^32 + MagicNumber)
结果向上取整
|
有符号除法
除数为正2的幂
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d \r\n", argc / 8);
return 0;
}
|
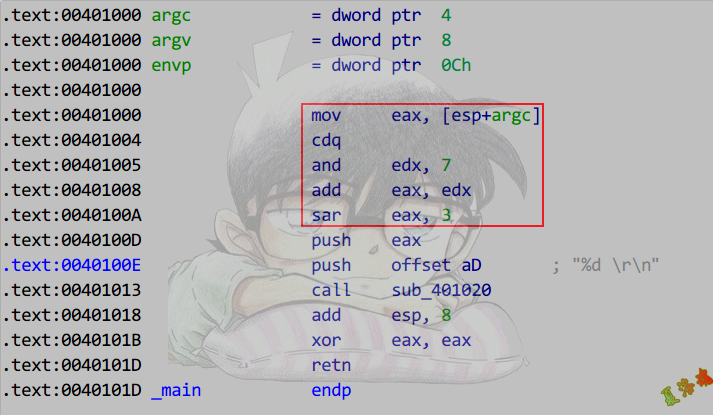
推导
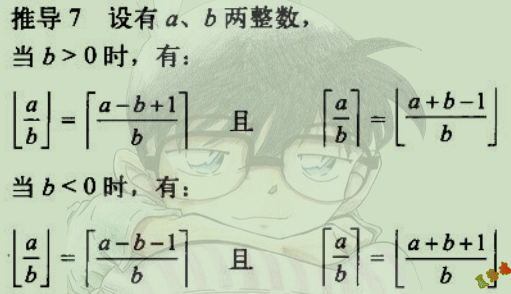
特征
1
2
3
4
5
|
mov eax, 被除数
cdq
and edx, 2 ^ n - 1
add eax, edx
sar eax, n
|
还原
除数为正非2的幂
MagicNumber为正
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d \r\n", argc / 5);
return 0;
}
|
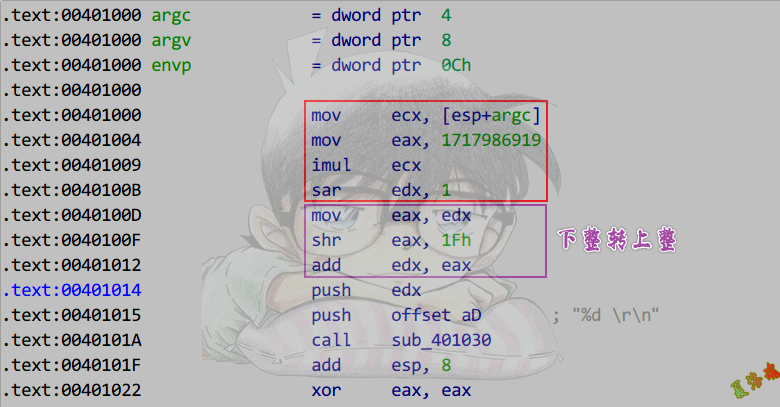
推导

特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
mov reg, 被除数
mov eax, MagicNumber ;(MagicNumber <= 0x7FFFFFFF)
imul reg
sar edx, n ;没有这条指令则指数为32
mov reg, edx
shr reg, 1Fh
add edx, reg
;此后直接使用edx的值
MagicNumber为正
乘法和移位之间无调整
|
还原
1
2
|
除数 = 2^(32 + n) / MagicNumber
结果向上取整
|
MagicNumber为负
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d", argc / 73);
return 0;
}
|
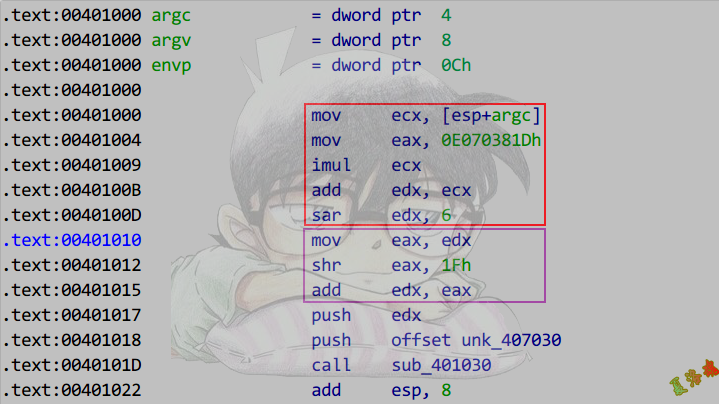
推导
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
在16位机器上计算无符号数0x8086与有符号数A,保证计算结果正确.
0x8086用imul指令会被当做负数,用补码进行计算
计算机计算= - ~0x8086 * A
= - (0x10000 - 0x8086) * A
=(0x8086 - 0x10000) * A
=0x8086 * A - 0x10000 * A
而我们想要得到0x8086 * A,故计算出来的结果应加上0x10000 * A
对应上图中的add edx, ecx
|
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
mov reg, 被除数
mov eax, MagicNumber ;(MagicNumber > 7FFFFFFFh)
imul reg
add edx, reg
sar edx, n ;没有这条指令则指数为32
mov reg, edx
shr reg, 1Fh
add edx, reg
;此后直接使用edx的值
MagicNumber为负
乘法和移位之间有加调整
|
还原
1
2
|
除数 = 2^(32 + n) / MagicNumber
结果向上取整
|
除数为负2的幂
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d", argc / -8);
return 0;
}
|
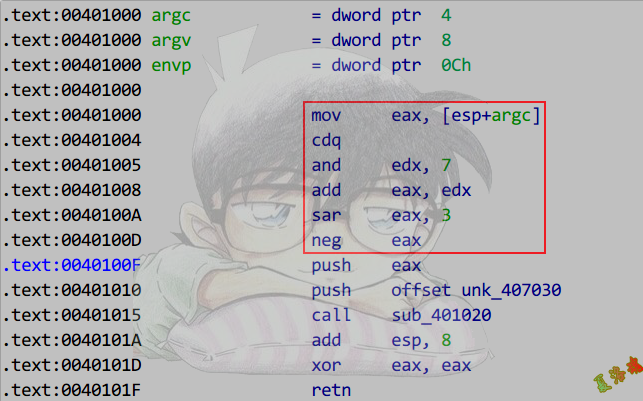
推导

特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
mov eax, 被除数
cdq
and edx, 2^n - 1
add eax, edx
sar eax, n
neg eax
|
还原
除数为负非2的幂
MagicNumber为正
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d", argc / -73);
return 0;
}
|
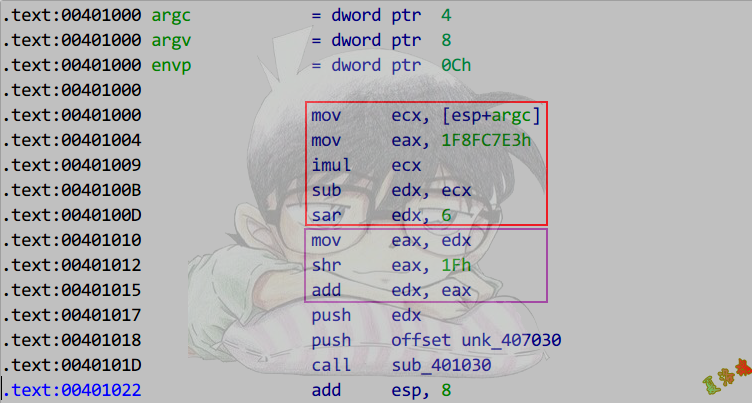
推导
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
在16位机器上计算无符号数0x8086与有符号数A,保证计算结果正确.
0x8086用imul指令会被当做负数,用补码进行计算
计算机计算= - ~0x8086 * A
= - (0x10000 - 0x8086) * A
=(0x8086 - 0x10000) * A
=0x8086 * A - 0x10000 * A
假设上面0x8086为MagicNumber
我们的MagicNumber为正,故-0x8086假定是MagicNumber
所以上面的计算机计算结果应加上符号,变为
-(0x8086 * A - 0x10000 * A)
=-0x8086 * A + 0x10000 * A
但我们想得到-0x8086 * A,故应再加上0x10000 * A
对应上图中的sub edx, ecx
|
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
mov reg, 被除数
mov eax, MagicNumber
imul reg
sub edx, reg
sar edx, n ;没有这句, 指数为32
mov reg, edx
shr reg, 1Fh
add edx, eax
;此后使用edx的值
MagicNumber为正
乘法和移位之间有减调整
|
还原
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
先将MagicNumber求补(取反+1)拿到原来的MagicNumbeSrc
除数的绝对值 = 2^(32 + n) /MagicNumberSrc
结果向上取整
除数为负
由于MagicNumber为正,故求补得到的MagicNumberSrc为负
注意参与计算的MagicNumSrc应当做无符号数进行计算
本例中MagicNumber = 0x1F8FC7E3
MagicNumberSrc = 0xE070381D, 对应的无符号十进制数为3765450781
故除数的绝对值 = 2^38 / 3765450781
结果向上取整为73
再添加负号就还原了除数为-73
|
MagicNumber为负
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d", argc / -5);
return 0;
}
|
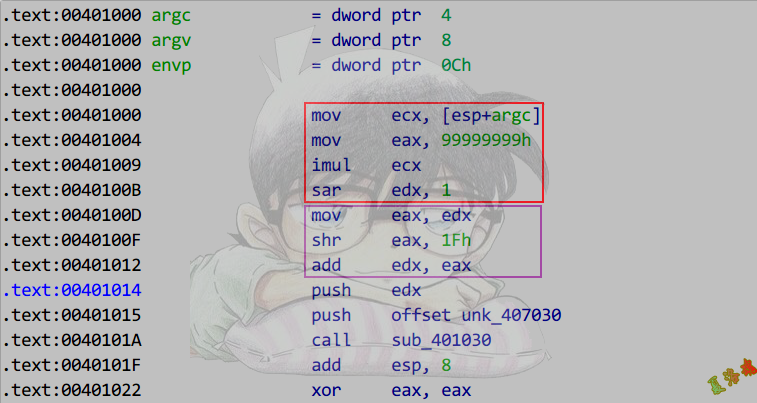
推导
1
2
3
4
|
A/(-C),C>0
-> -A * M >> n
-> A * -M >> n
故汇编显示的MagicNumber为原来MagicNumber求补后的结果.
|
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
mov reg, 被除数
mov eax, MagicNumber
imul reg
sar edx, n ;没有这句, 指数为32
mov reg, edx
shr reg, 1Fh
add edx, reg
;此后使用edx的值
MagicNumber为负
乘法和移位之间没有调整
|
还原
1
2
3
4
|
先将MagicNumber求补(取反+1)拿到原来的MagicNumbeSrc
除数的绝对值 = 2^(32 + n) /MagicNumberSrc
结果向上取整
除数为负
|
取模
基础
模的符号与被除数相同.
除数为变量,无优化,只有当除数为常量时,才有优化空间.
无符号取模
除数为2的幂
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(unsigned int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d\r\n", argc % 8);
return 0;
}
|
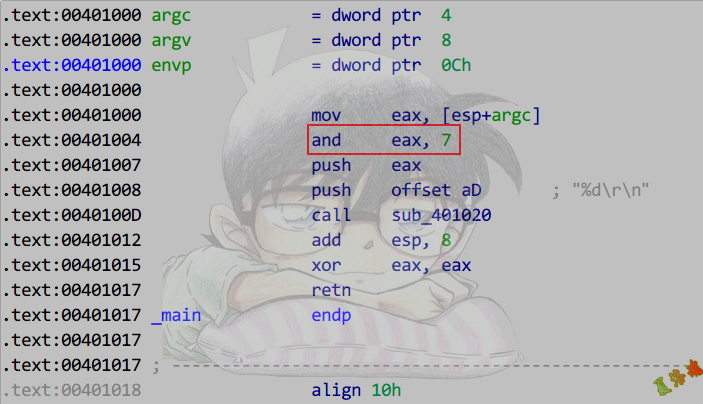
推导
1
2
|
对2的n次方取模,实际上是取该数值的二进制低n位
如10进制中,321%100,我们取321的低2位,就可以知道余数为21
|
特征
1
2
|
mov reg, 被除数
and reg, 2 ^ n - 1
|
还原
除数为非2的幂
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(unsigned int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d\r\n", argc % 7);
return 0;
}
|
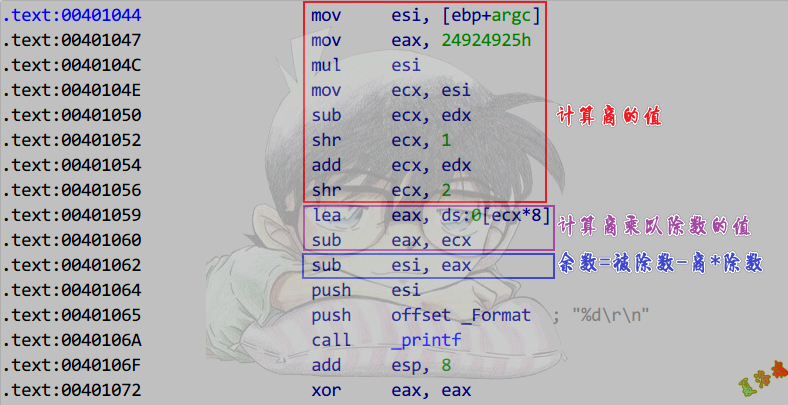
推导
还原
1
2
|
可以通过上面的除法部分得到除数
也可以通过中间商乘以除数的部分得到除数
|
有符号取模
除数为正2的幂
带分支
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d\r\n", argc % 8);
return 0;
}
|
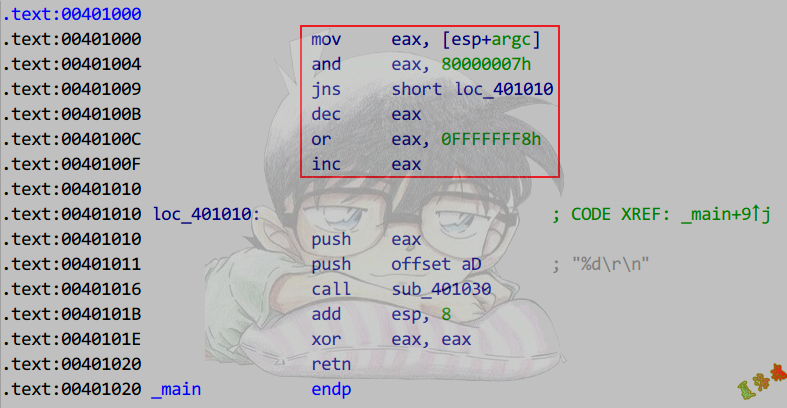
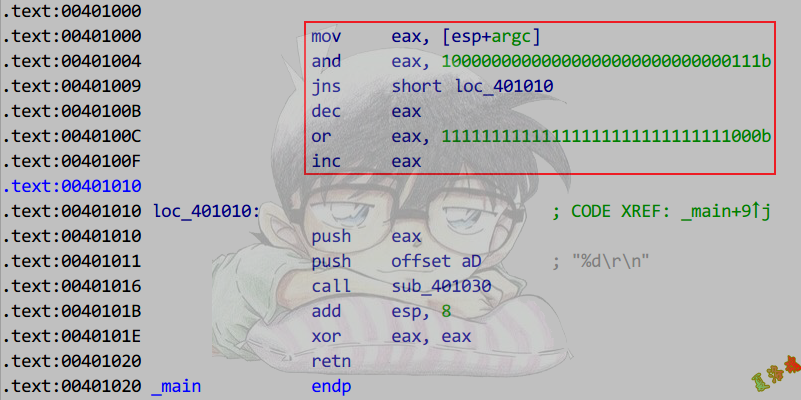
推导
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
mov eax, [esp+argc] ;将被除数给eax
and eax, 80000007h ;取被除数的符号位和低n位
jns short loc_401010 ;如果被除数为正,跳走,直接使用eax
dec eax ;处理负数取模为0的情况 减1后为全f,如果取模不为0的情况是不需要dec和inc指令
or eax, 0FFFFFFF8h ;被除数为负,需要将模的结果高位填补为1
inc eax ;处理负数取模为0的情况 上面减后全为f,此处加1,调整为0
loc_401010:
;使用eax
|
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
mov reg, 被除数
and reg, 0x8000000(2^n - 1)
jns LABLE
dec reg
or reg, 0xFFFFFFF(2^n)
inc reg
LABLE:
;使用reg
|
还原
不带分支
见除数为负2的幂.
除数为正非2的幂
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d\r\n", argc % 7);
return 0;
}
|
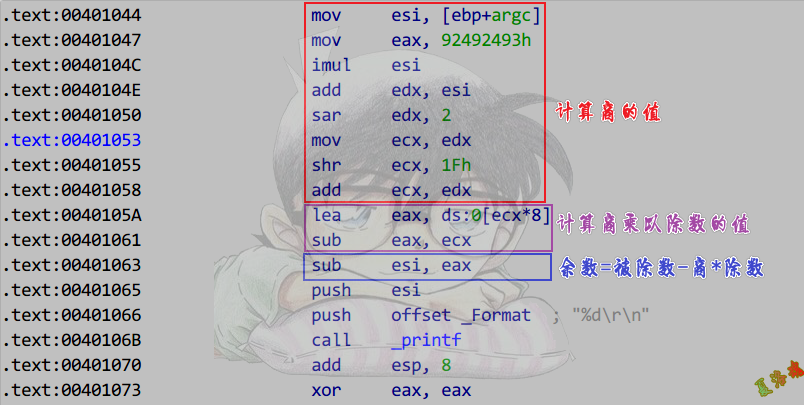
推导
还原
1
2
|
可以通过上面的除法部分得到除数
也可以通过中间商乘以除数的部分得到除数
|
除数为负2的幂
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d\r\n", argc % -8);
return 0;
}
|
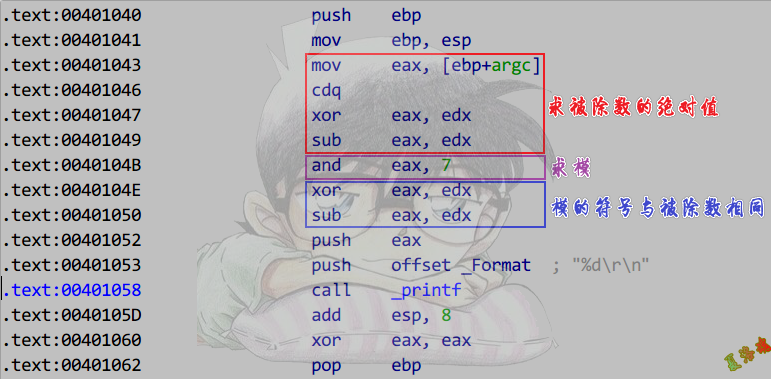
推导
1
2
|
对2的n次方取模,实际上是取该数值的二进制低n位
模的符号与被除数相同
|
还原
1
2
|
上图中的7为2^n - 1
除数 = 2^n
|
除数为负非2的幂
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d\r\n", argc % -7);
return 0;
}
|
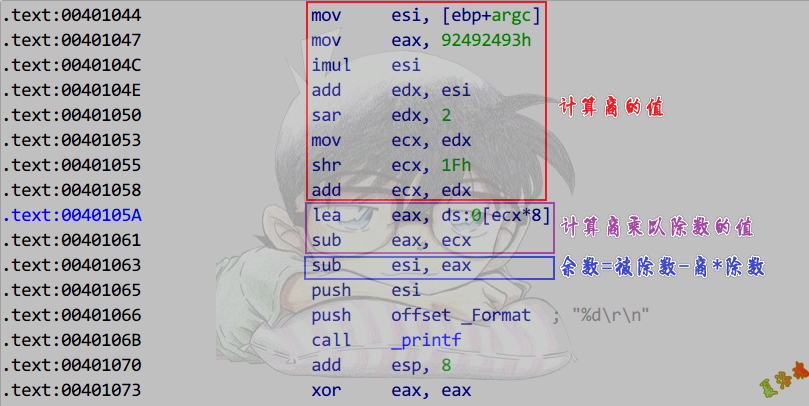
推导
还原
1
2
|
可以通过上面的除法部分得到除数
也可以通过中间商乘以除数的部分得到除数
|
三目运算
基础
表达式1 ? 表达式2 : 表达式3,只有当表达式2和表达式3为常量时,才可以优化,否则和if分支语句产生的代码一样.
低版本优化
原型:
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d\r\n", argc == 0 ? 0 : -1);
return 0;
}
|
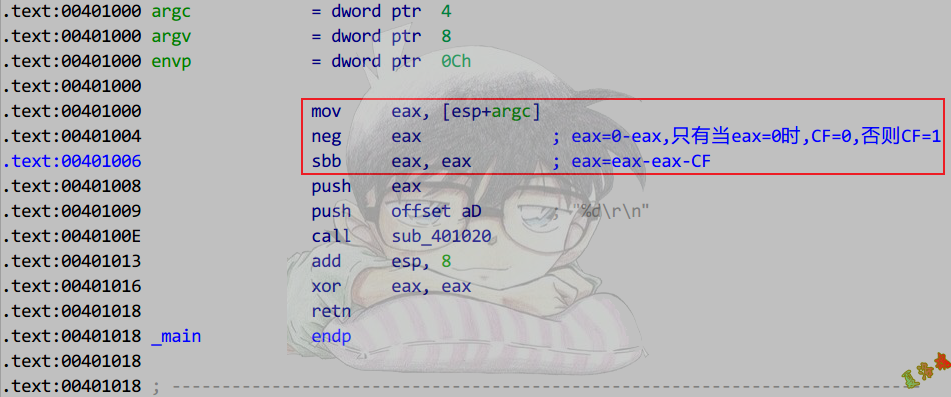
特征
1
2
3
|
mov reg, 表达式1中的第1项值
neg reg
sbb reg, reg
|
演变1:
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d\r\n", argc == 100 ? 6 : 2);
return 0;
}
|
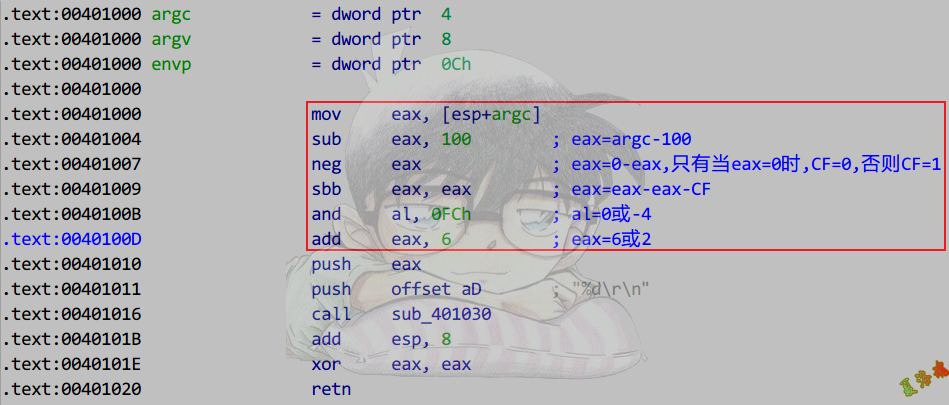
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
mov reg,表达式1第一项值
sub reg, 表达式1第二项值
neg reg
sbb reg, reg
and rl, 表达式3-表达式2
add reg, 表达式2
|
演变2:
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d\r\n", argc > 100 ? 2 : 6);
return 0;
}
|
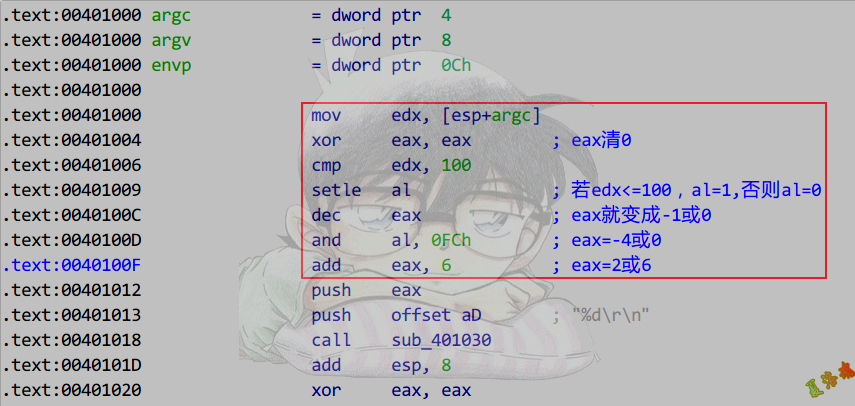
高版本优化
1
2
3
4
5
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%d\r\n", argc >= 100 ? 5 : 2);
return 0;
}
|
流程控制语句
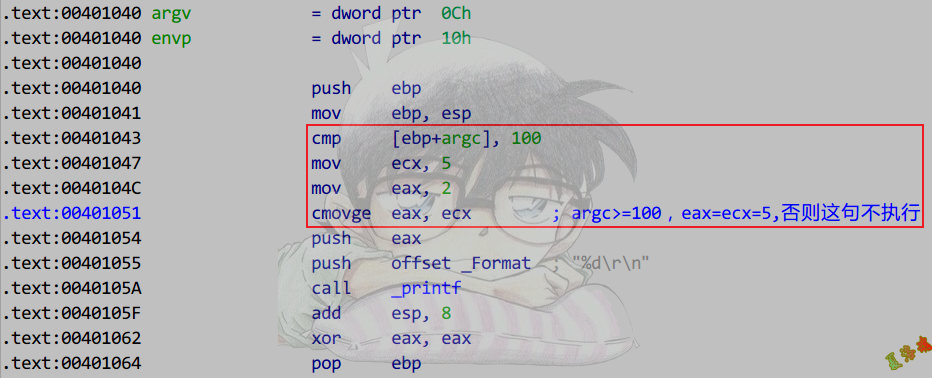
IF
单分支结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc > 10)
{
printf("argc > 10\r\n");
}
return 0;
}
|
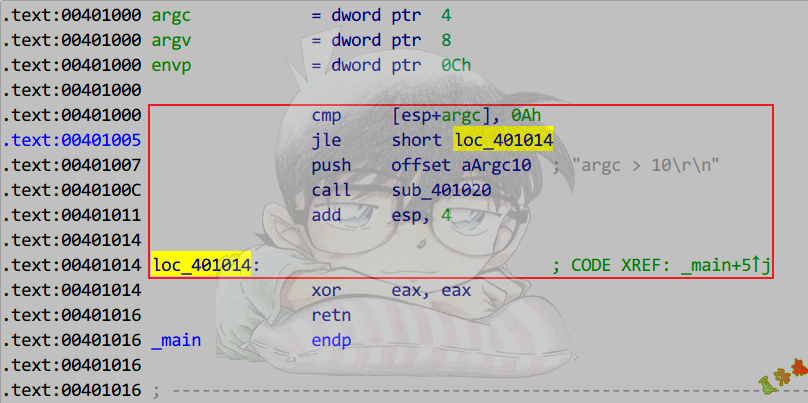
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
IF_BEGIN
jxx IF_END
.
. ;中间为条件体
. ;注意语句上面无跳转
IF_END
|
双分支结构
代码外提:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc > 10)
{
printf("argc > 10\r\n");
}
else
{
printf("argc <= 10\r\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
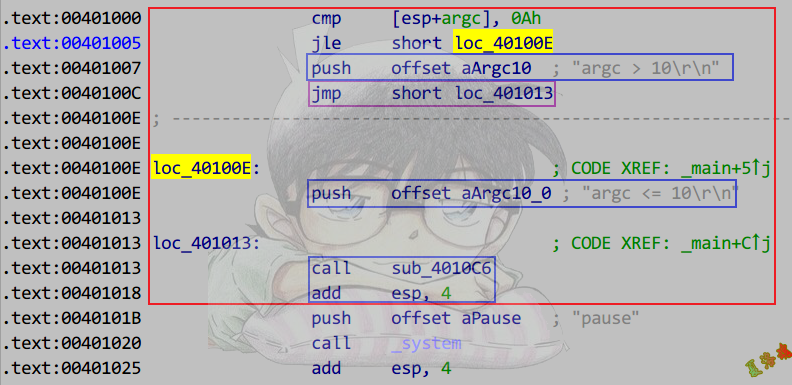
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
IF_BEGIN
jxx ELSE_BEGIN
...
IF_END
jmp ELSE_END
ELSE_BEGIN
...
ELSE_END
|
代码内提:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc > 10)
{
printf("argc > 10\r\n");
}
else
{
printf("argc <= 10\r\n");
}
return 0;
}
|
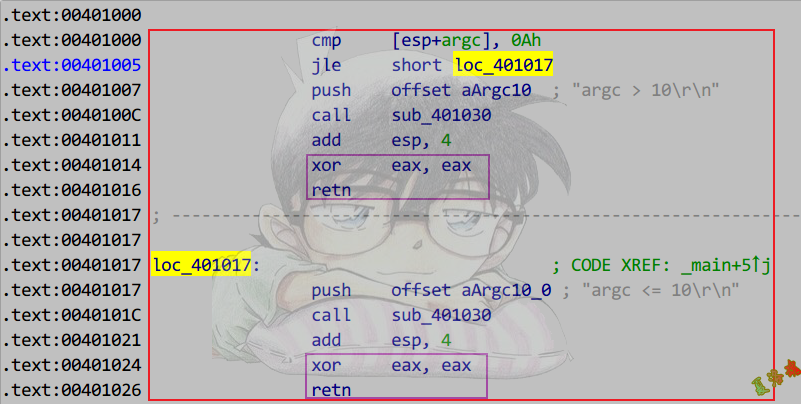
多分支结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc > 10)
{
printf("argc > 10\r\n");
}
else if (argc < 10)
{
printf("argc < 10\r\n");
}
else
{
printf("argc == 10\r\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
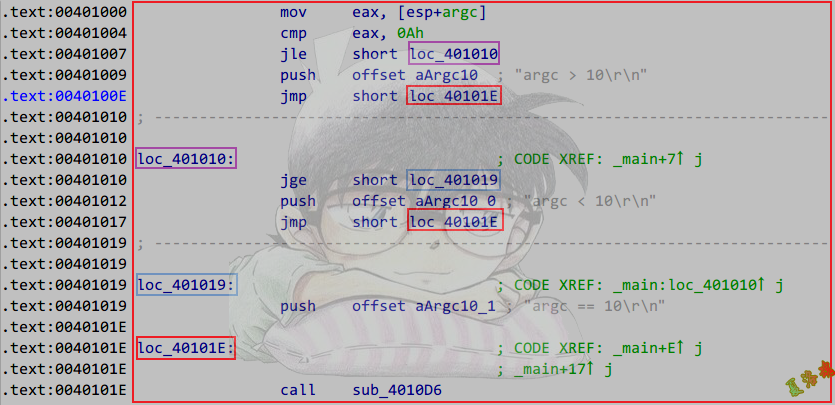
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
IF_BEGIN
jxx ELSE_IF_BEGIN
...
IF_END
jmp ELSE_END
ELSE_IF_BEGIN
jxx ELSE_BEGIN
...
ELSE_IF_END
jmp ELSE_END
ELSE_BEGIN
...
ELSE_END
|
SwitchCase
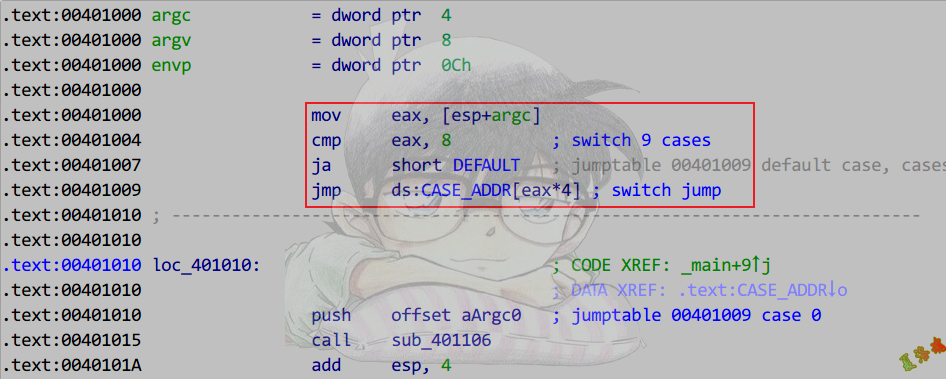
Case语句<=3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
switch (argc)
{
case 0:
printf("argc == 0\r\n");
case 1:
printf("argc == 1\r\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("argc == 2\r\n");
break;
default:
printf("default\r\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
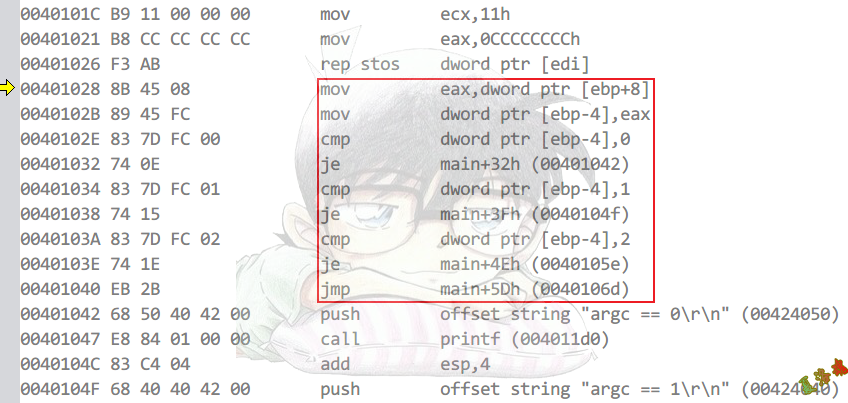
Release
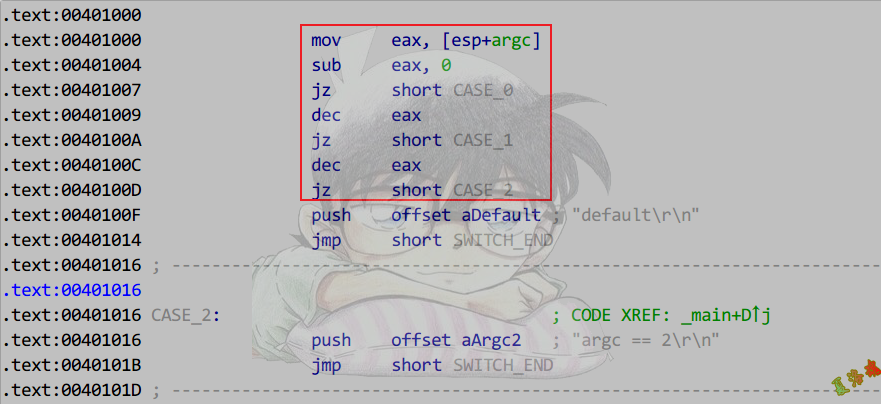
特征
1
2
|
一个个比较,中间无代码块
这样的话,匹配跳转成功时,没有break语句会继续向下执行
|
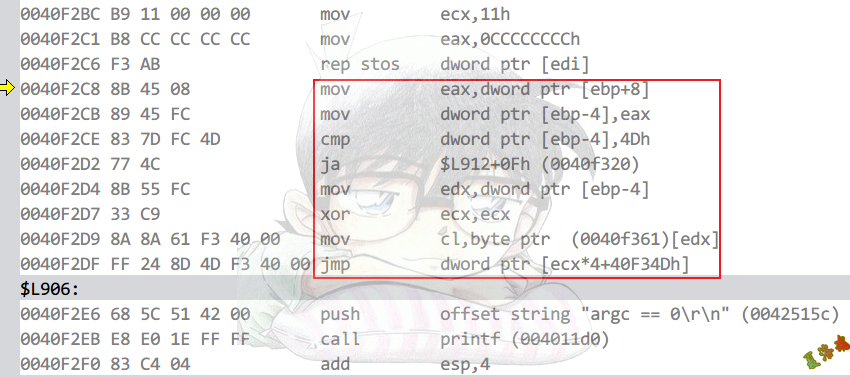
case语句>3,且每两个Case值之间的差值<=6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
switch (argc)
{
case 0:
printf("argc == 0\r\n");
case 1:
printf("argc == 1\r\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("argc == 2\r\n");
break;
case 8:
printf("argc == 8\r\n");
break;
default:
printf("default\r\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
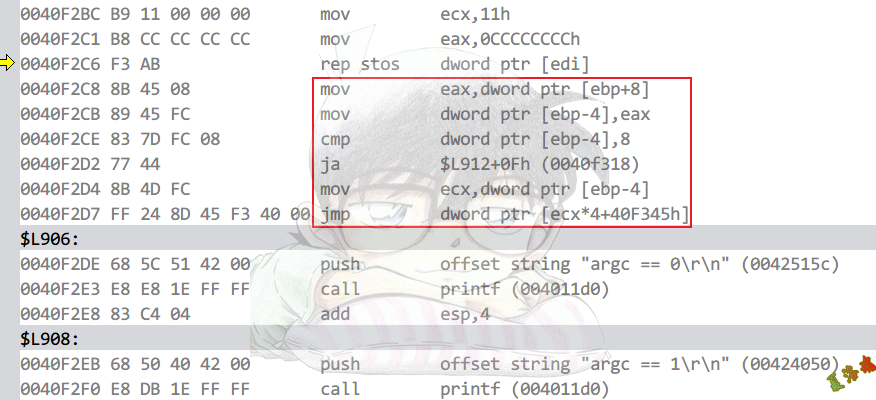
Release
特征
1
2
|
编译器会给所有case情况做一个表
当提供的序号大于最大索引时,直接跳转到DEFAULT或SWITCH_END
|
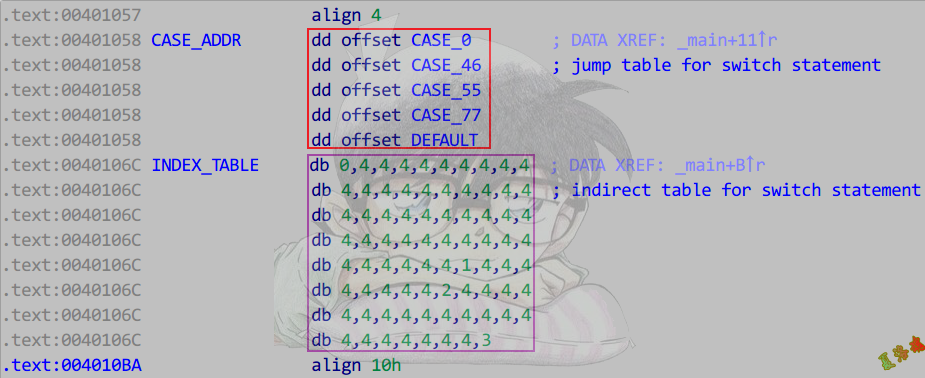
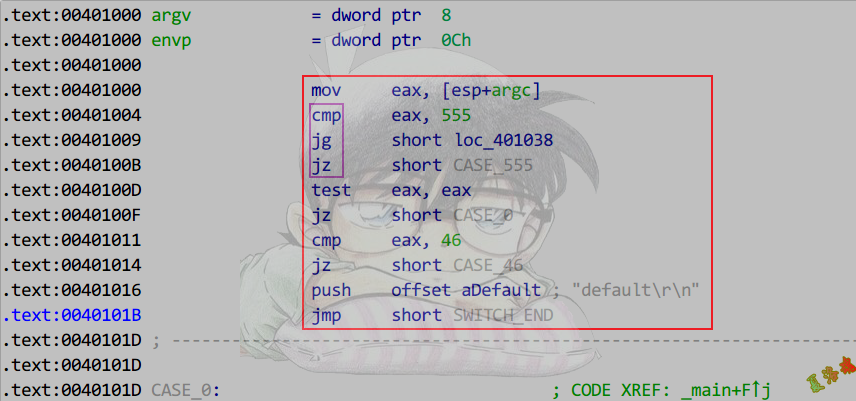
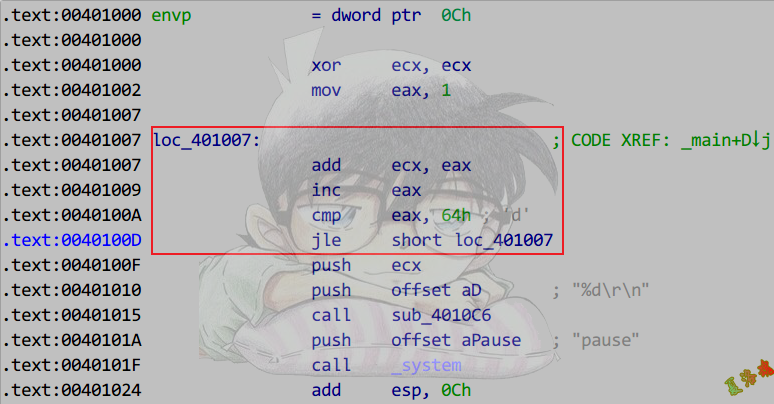
case语句>3,最大case值-最小case值<=255
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
switch (argc)
{
case 0:
printf("argc == 0\r\n");
case 46:
printf("argc == 46\r\n");
break;
case 55:
printf("argc == 55\r\n");
break;
case 77:
printf("argc == 77\r\n");
break;
default:
printf("default\r\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
Release
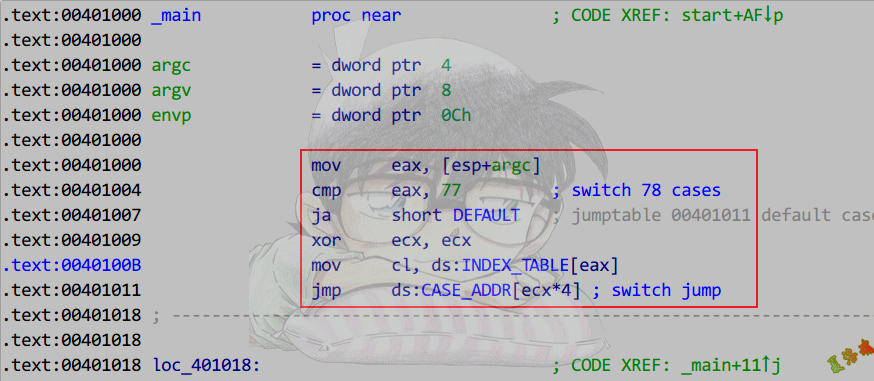
特征
1
2
3
|
编译器会生成两个表
下标表:记录对应case地址表的下标
case地址表:记录case语句块的地址
|
还原
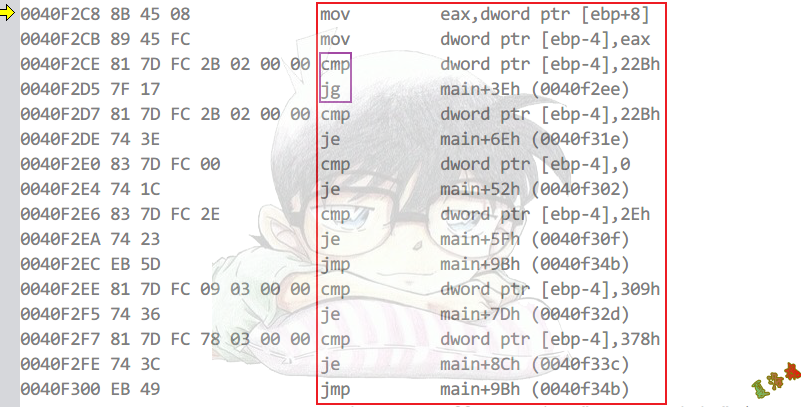
case语句>3,最大case值-最小case值>255
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
switch (argc)
{
case 0:
printf("argc == 0\r\n");
case 46:
printf("argc == 46\r\n");
break;
case 555:
printf("argc == 555\r\n");
break;
case 777:
printf("argc == 777\r\n");
break;
case 888:
printf("argc == 888\r\n");
break;
default:
printf("default\r\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
Release
特征
1
2
|
二分优化
注意:会进行二分优化和前面三种混合优化
|
注意
break语句,对应的跳转一定是跳向SWITCH_END.
循环语句
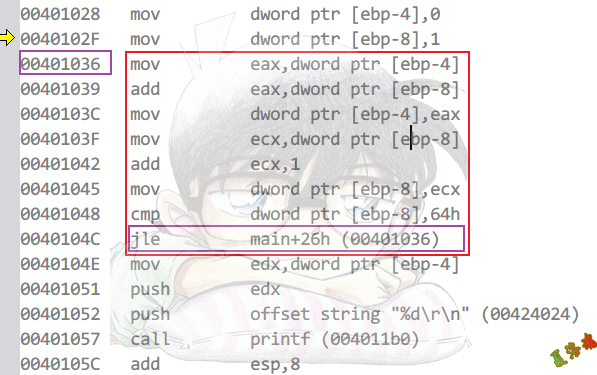
DoWhile
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int nSum = 0;
int n = 1;
do
{
nSum += n;
n++;
} while (n <= 100);
printf("%d\r\n", nSum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
Release
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
Do_Begin
...
...
...
jxx Do_Begin
Do_End
|
While
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int nSum = 0;
while (argc <= 100)
{
nSum += argc;
argc++;
}
printf("%d\r\n", nSum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
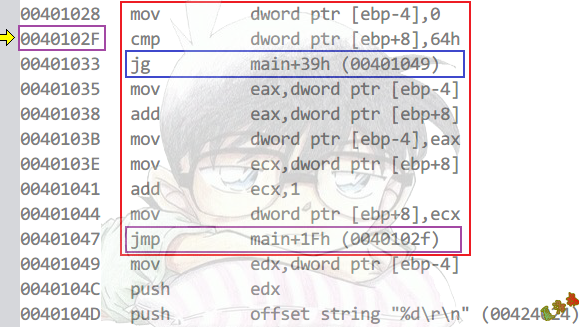
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
While_Begin
jxx While_End
...
...
...
jmp While_Begin
While_End
|
Release
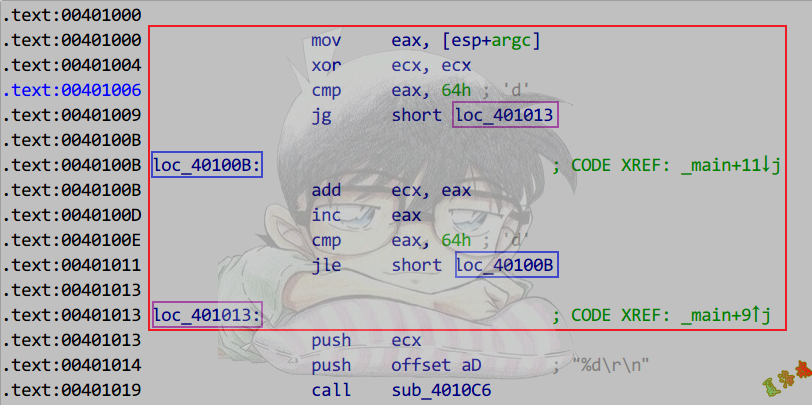
特征
1
2
3
|
这个地方While循环会被优化成DoWhile循环
多了一个跳转提前进行判断
注意:跳转的判定条件和循环的判定条件具有相关性时,才可还原为While循环
|
For
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int nSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
nSum += i;
}
printf("%d\r\n", nSum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
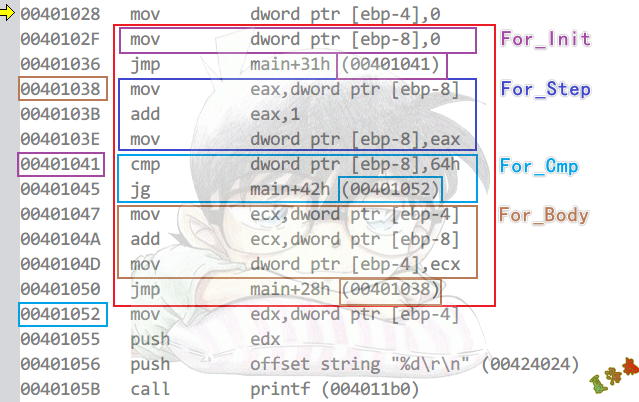
特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
For_Init
...
jmp For_Cmp
For_Step
...
For_Cmp
jxx For_End
For_Body
...
...
jmp For_Step
For_End
|
Release
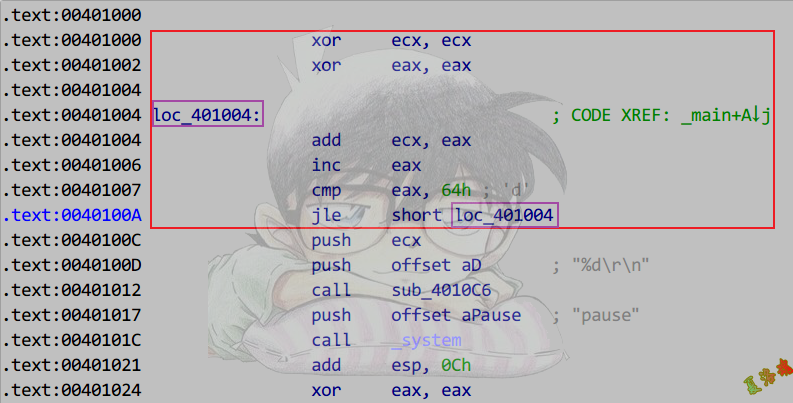
特征
注意
//Break语句
循环语句中,跳转循环体,可识别为break语句
//Continue语句
Release版,经常会将Continue语句优化为If_Else双分支结构
函数调用方式
_cdecl
1
2
3
|
C\C++默认的调用方式
调用方平栈
参数:从右到左以此入栈
|
_stdcall
_fastcall
1
2
|
被调方平栈
参数:前两个参数由寄存器传递(VS编译器用edx, ecx),其余参数通过堆栈传递
|
变量相关
全局变量
特征:
- 所在地址为数据区,生命周期与所在模块一致.
- 使用立即数访问.
全局变量初始化:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
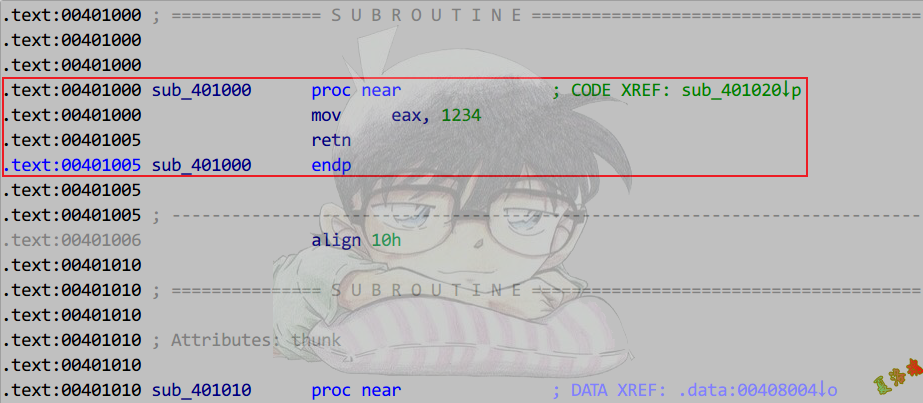
int foo()
{
return 1234;
}
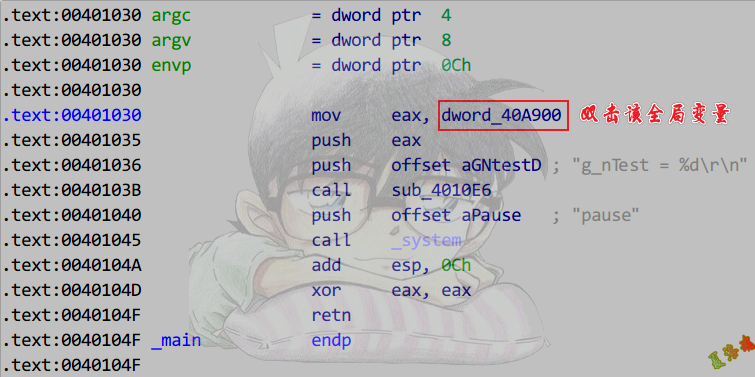
int g_nTest = foo();
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("g_nTest = %d\r\n", g_nTest);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
定位初始化位置
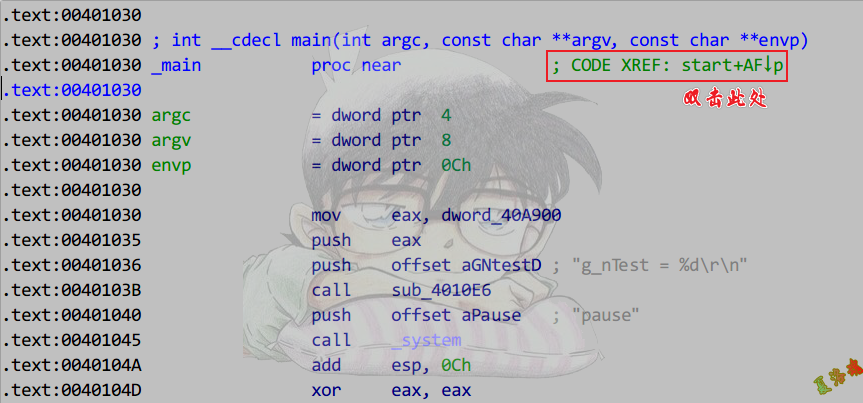
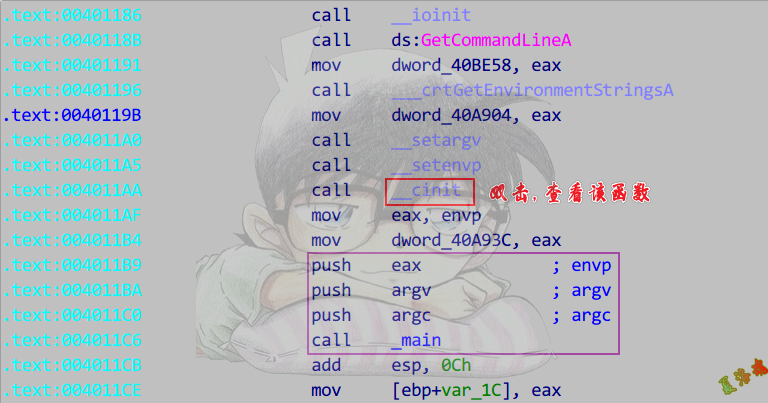
注意:高版本_cinit函数被内联了.
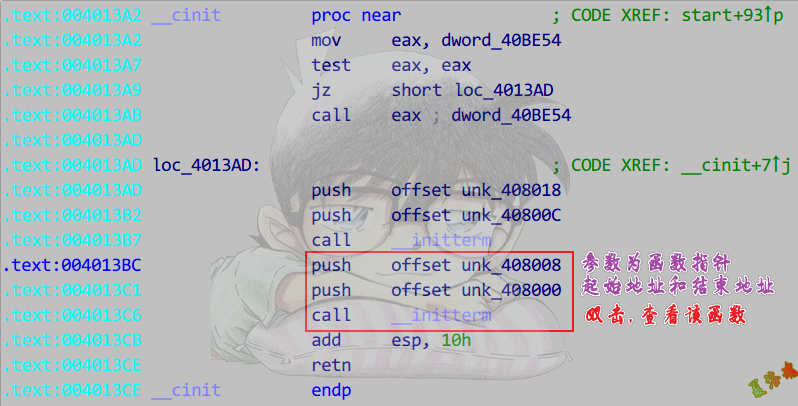
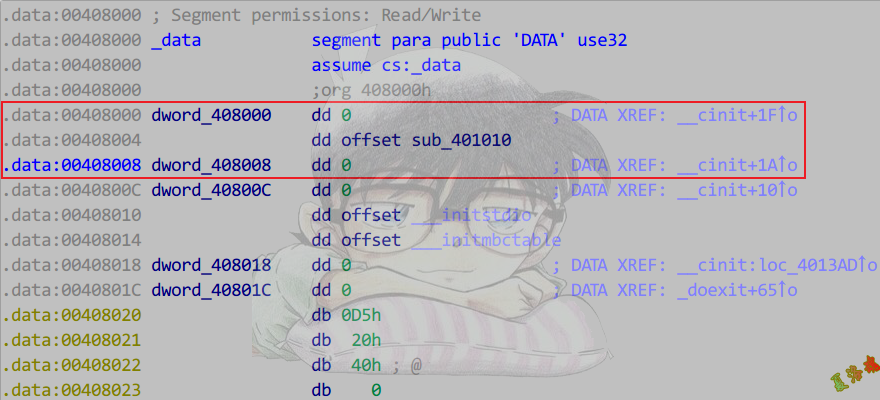
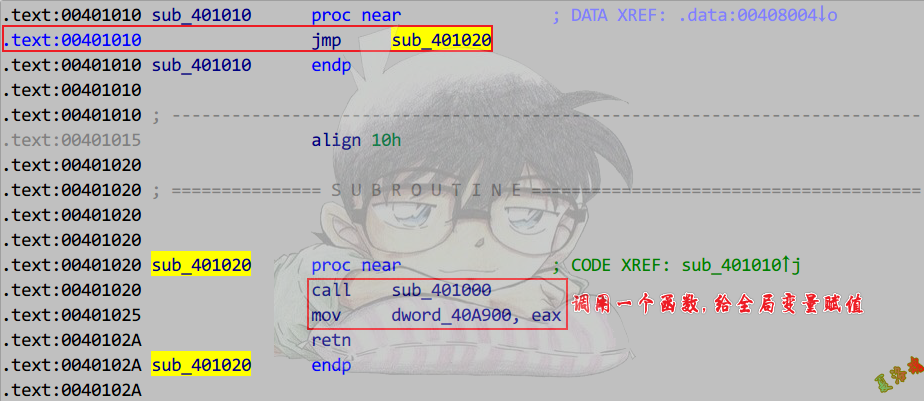
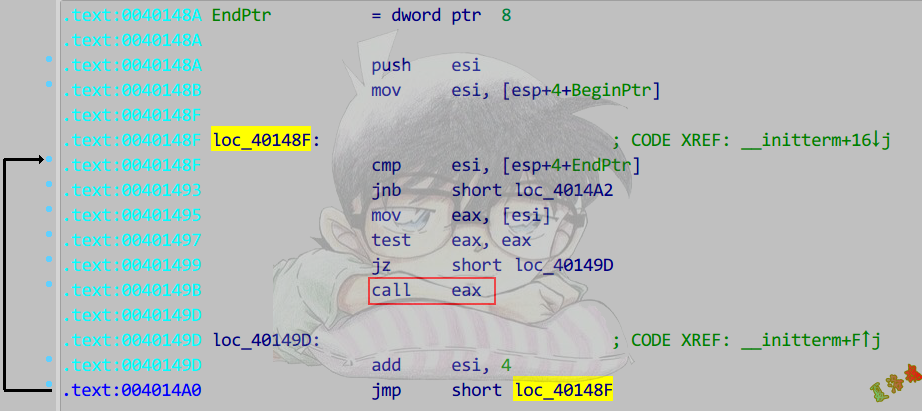
使用交叉引用
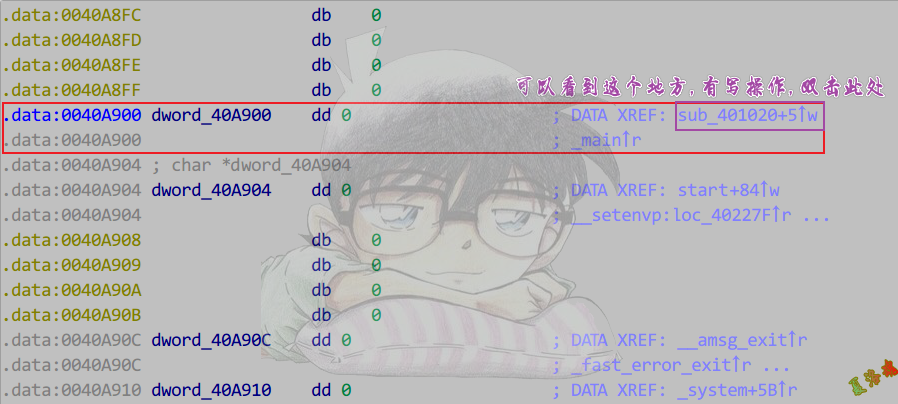
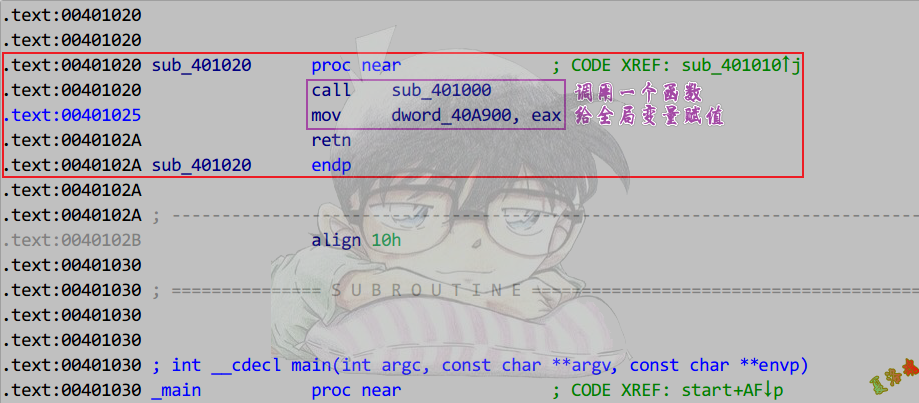
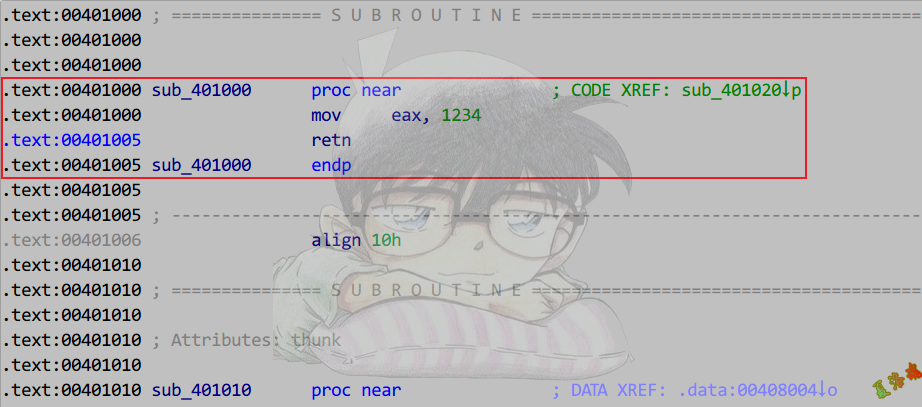
局部变量
特征:
- 所在地址为栈区,生命周期与所在的函数作用域一致.
- 使用ebp或esp间接访问.
局部静态变量
C++语法规定局部静态变量只被初始化一次.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
static float f = 3.14f / argc;
printf("f = %f\r\n", f);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
VC6.0Release版
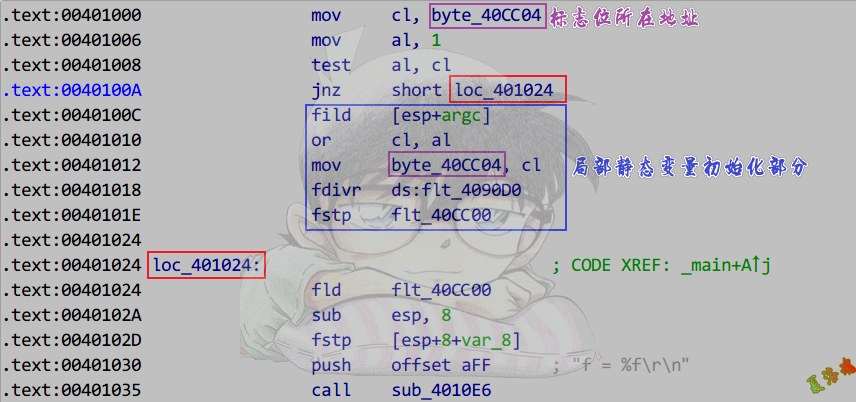
高版本(如VS2019)将这个标志位放到了Tls中.
堆变量
在C\C++中,使用malloc与new实现堆空间的申请.
X87浮点指令集
VC6.0 ~ VS2013.
特征
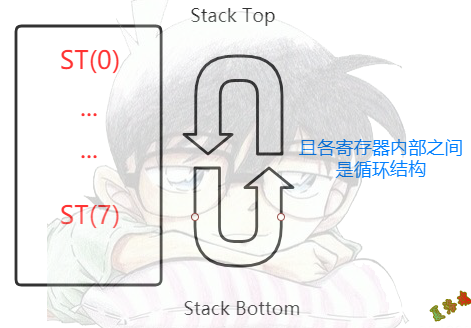
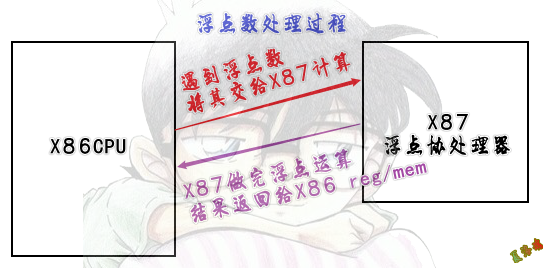
- 使用80位浮点协处理器处理浮点运算.
- 浮点协处理器内部为栈结构.
运算过程
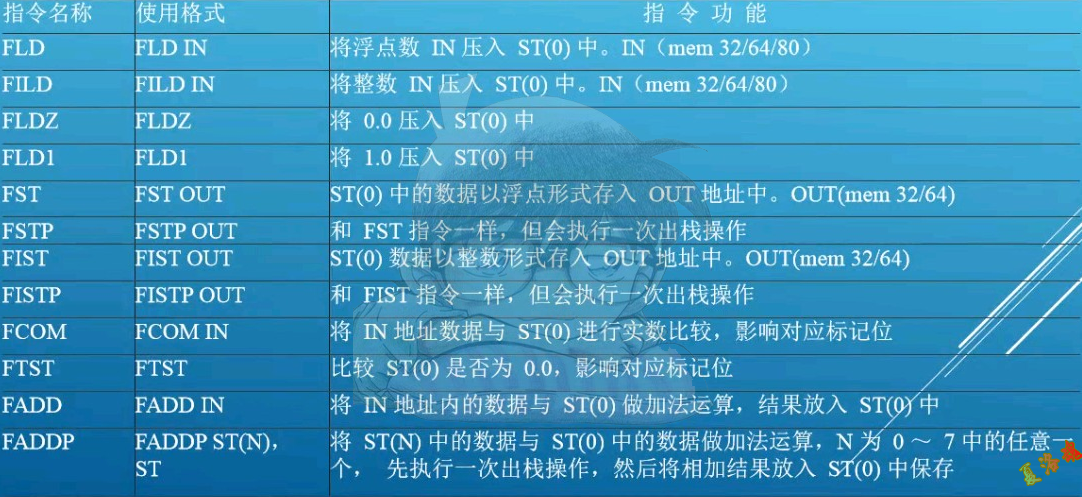
指令
探测浮点标志位
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
float f = 3.14f / argc;
if (f == (float)argc) //ZF = 1
{
printf("f == (float)argc\r\n");
}
else //ZF = 0
{
printf("f != (float)argc\r\n");
}
if (f > 1.23f) //SF = 0 and ZF = 0
{
printf("f > 1.23f\r\n");
}
else //SF = 1 or ZF = 1
{
printf("f <= 1.23f\r\n");
}
if (f < 1.23f) //SF = 1
{
printf("f < 1.23f\r\n");
}
else
{
printf("f >= 1.23f\r\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
参考资料
Intel奔腾指令速查手册.doc
多媒体指令集
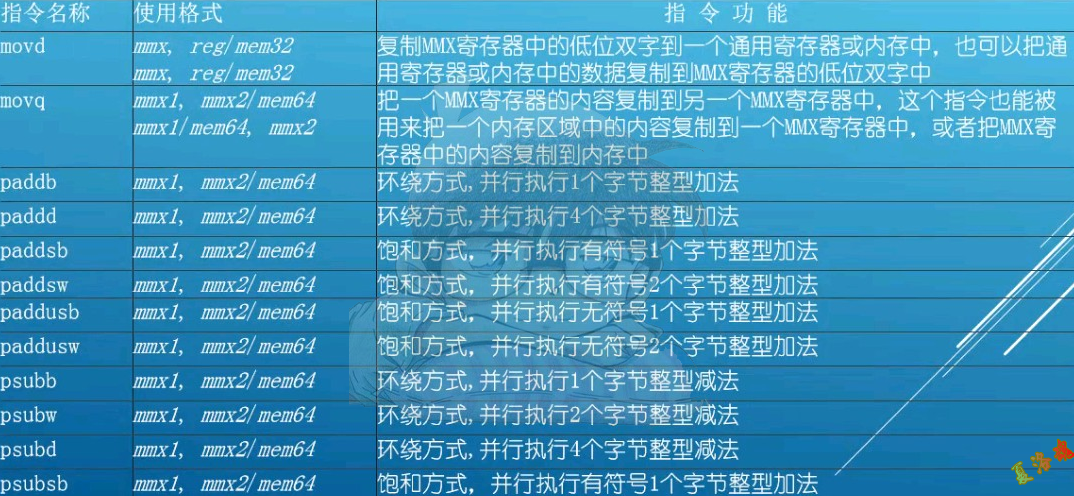
MMX
VS中使用MMX指令,包含头文件mmintrin.h
特征如下:
- 有8个64位寄存器(MM0~MM7),借用的是FPU原来的8个80位寄存器(st(0)~st(7)),故使用MMX指令后,需要加上一条EMMS指令,用以复位.
- 不再使用栈结构.
- 寄存器在拆分做独立运算时有两种模式.
- 支持并行计算.
指令
详细查看AMD开发手册(卷5).
SSE
VS中使用SSE指令
1
2
3
4
|
xmmintrin.h //SSE
emmintrin.h //SSE2
pmmintrin.h //SSE3
smmintrin.h //SSE4
|
特征如下:
- 有8个128位独立寄存器(XMM0~XMM7).
- 支持并行计算.
指令
详情查看AMD开发手册(卷4).


AVX
VS中使用AVX指令,包头文件immintrin.h
特征如下:
- 扩展之前的8个128位寄存器为8个256位寄存器(YMM0~YMM7).
- 支持并行计算.
指令
相对于SSE指令语法,前缀加v即可.
VS中设置多媒体指令集
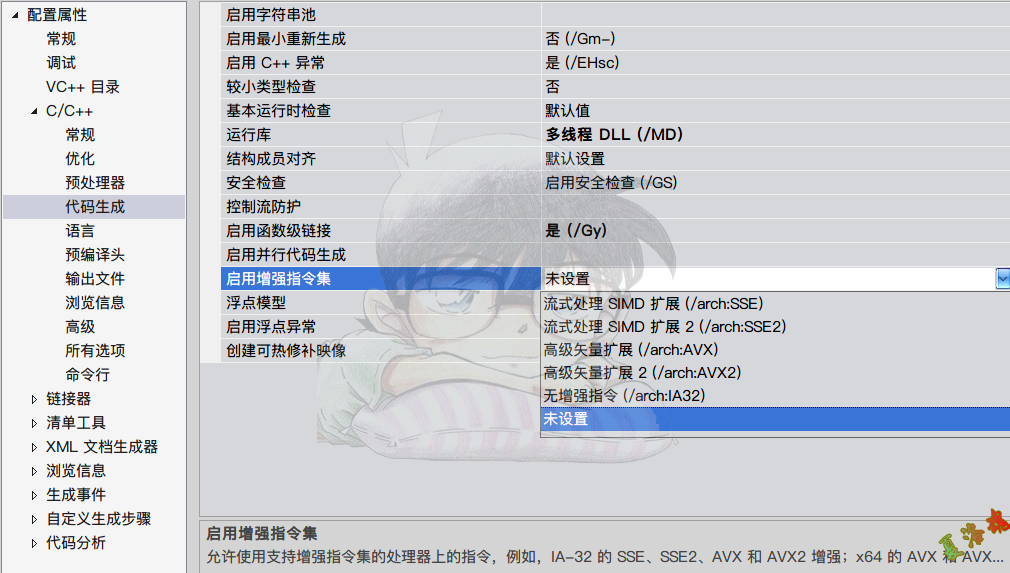
数组
特性:
连续性:数组内元素连续排列,且互相不会覆盖.
一致性:具备同类业务功能,即类型和业务功能一样.
注意:身高,体重,年龄都是int类型,但数据功能代表的不一样,这种不属于数组,属于结构体.
体现数组特性:
一维数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int ary[5] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 };
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%d\r\n", ary[i]);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
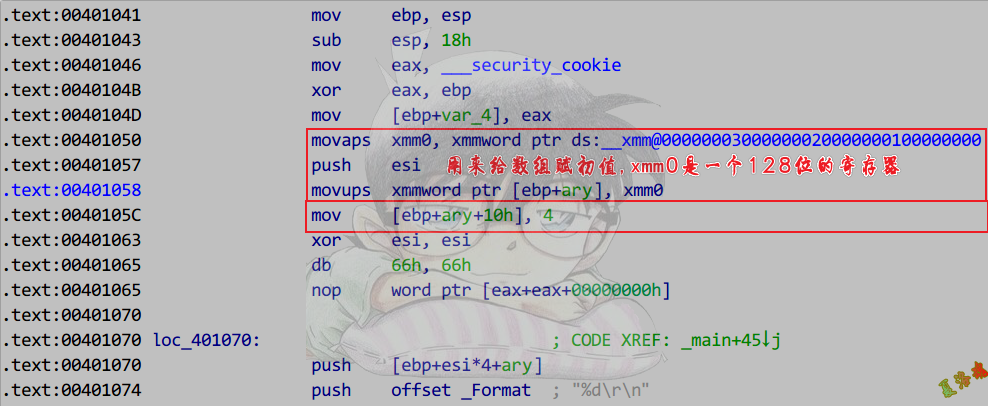
Debug
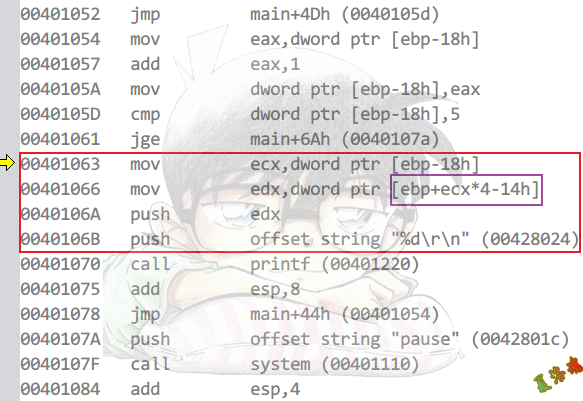
Release
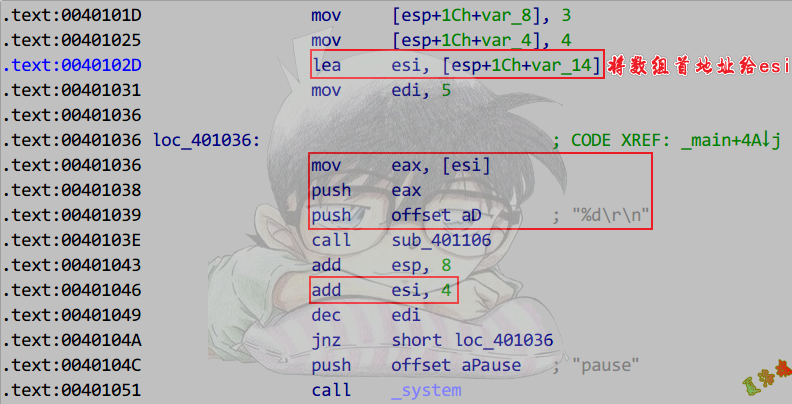
高版本(VS2015)Release
数组寻址公式
1
2
3
|
假设数组为ary[n]
ary[x]寻址:
数组首地址 + x * sizeof(type)
|
二维数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int ary[3][5] = {
{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 },
{ 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 },
{ 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 }
};
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\r\n", ary[x][y]);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
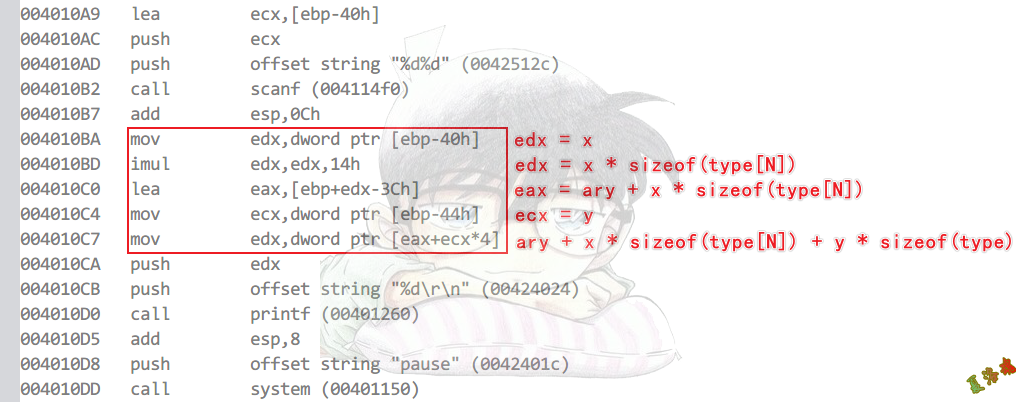
Release
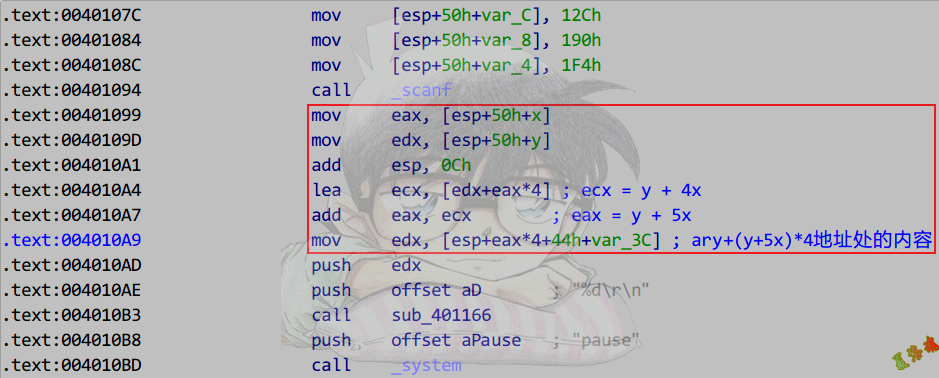
数组寻址公式
1
2
3
4
|
假设数组为ary[M][N]
ary[x][y]寻址
Debug版:ary + x * sizeof(type[N]) + y * sizeof(type)
Release版:ary + (x * N + y) * sizeof(type)
|
三维数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int ary[2][3][5] = {
{
{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 },
{ 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 },
{ 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 }
},
{
{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 },
{ 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 },
{ 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 }
}
};
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int z = 0;
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &z);
printf("%d\r\n", ary[x][y][z]);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
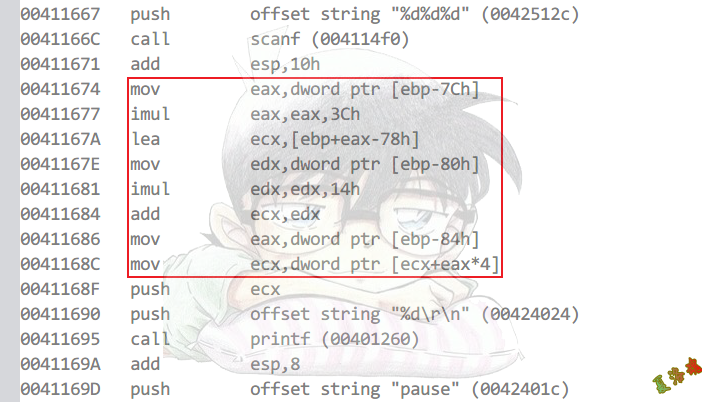
Release
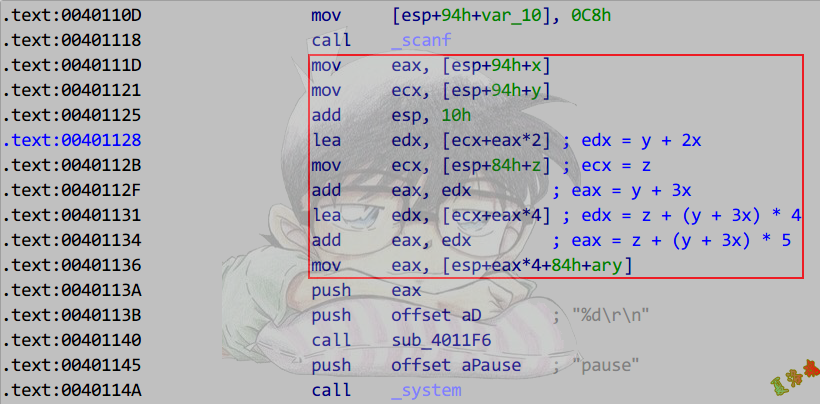
数组寻址公式
1
2
3
4
|
假设数组为ary[M][N][K]
ar[x][y][z]寻址
Debug版:ary + x * sizeof(type[N][K]) + y * sizeof(type[K]) + z * sizeof(type)
Release版:ary + ((x * N + y) * K + z) * sizeof(type)
|
结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
struct tagTest
{
char szName[5]; // + 0
int n; // + 8
double dbl; // + 16
short int w; // + 24
float f; // + 28
}; // sizeof 32
|
指针访问结构体成员
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
tagTest t = {
"Luo",
1234,
3.14,
12,
0.618f
};
tagTest* p = &t;
printf("%d\r\n", p->n);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
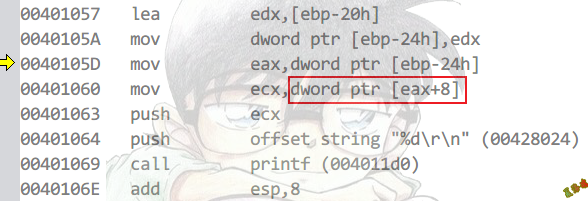
特征
1
2
3
|
会出现寄存器相对间接寻址
出现这种情形,只能是数组常量下标访问或结构成员访问
识别的关键在于论证其中的元素是否具备存储连续性,以及作用是否一致
|
参数为结构体变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
void foo(struct tagTest t)
{
printf("%d\r\n", t.n);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
tagTest t = {
"Luo",
1234,
3.14,
12,
0.618f
};
foo(t);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
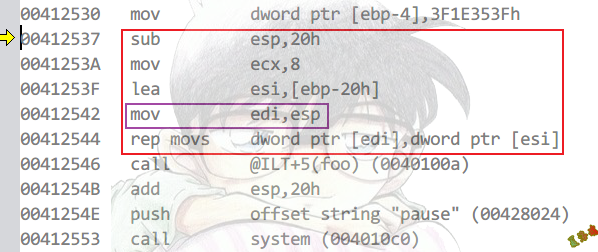
高版本(VS2019)
会使用多媒体指令集完成,如果结构体足够大,就会使用内联memcpy分方式拷贝到栈上.
特征
1
2
3
|
会将结构体内容拷贝到栈上
关键语句:mov edi, esp
其实相当于一个内联的memcpy(esp, addr, size)
|
参数为结构体指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
void foo(struct tagTest* pt)
{
printf("%d\r\n", pt->n);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
tagTest t = {
"Luo",
1234,
3.14,
12,
0.618f
};
foo(&t);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
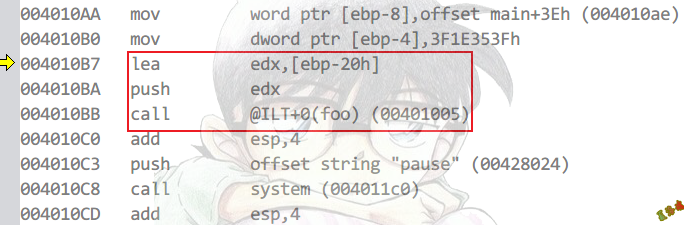
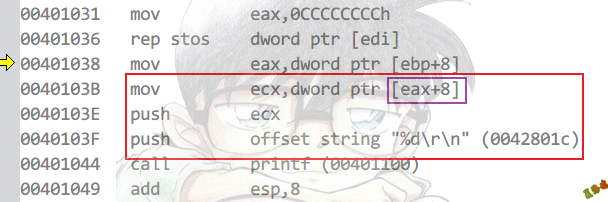
特征
访问的时候,会出现寄存器相对间接寻址.
函数返回值为结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
tagTest foo()
{
tagTest t = {
"Luo",
1234,
3.14,
12,
0.618f
};
return t;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
tagTest t2 = foo();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
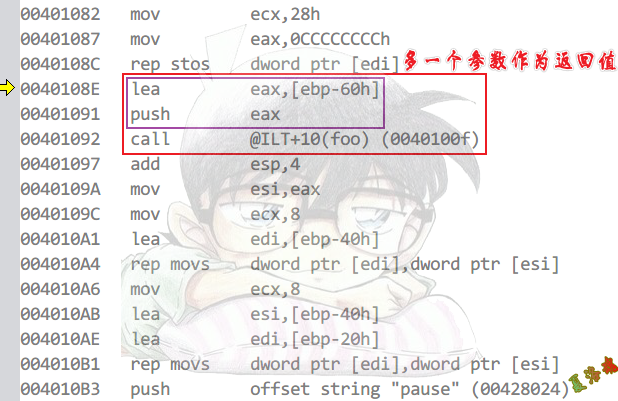
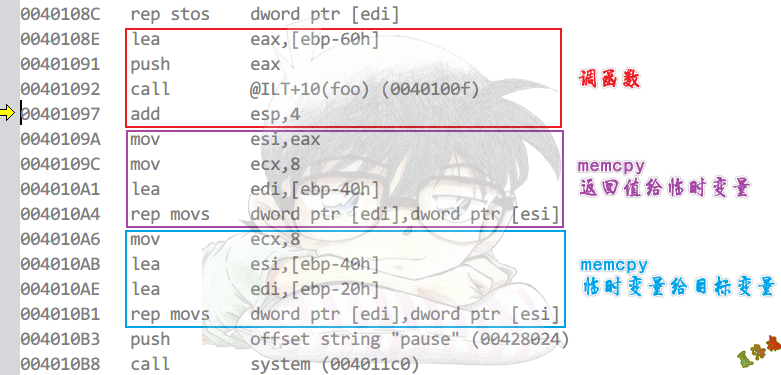
返回值给临时变量,因为我们有可能会访问返回值,如foo().n
特征
1
2
3
|
多一个参数返回结构体地址
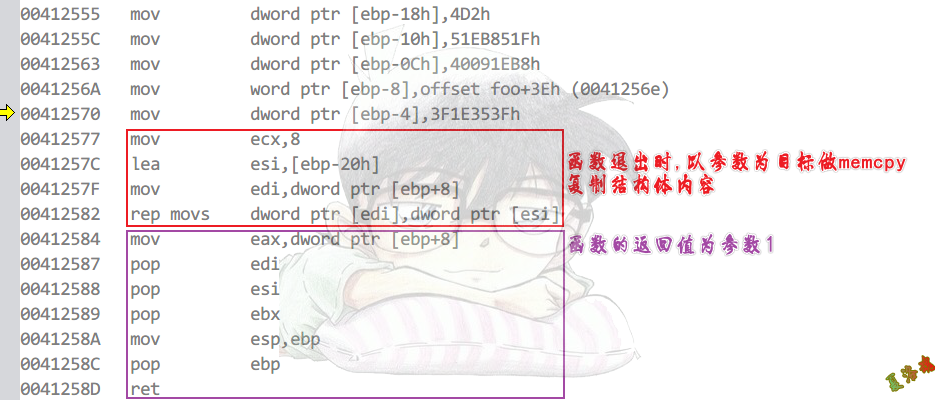
函数退出时,以参数为目标做memcpy复制结构体内容
函数的返回值为参数1
|
还原
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
我们按照汇编代码还原,可还原成以下结构
tagTest* GetObj(tagTest* p)
{
...
...
...
memcpy(p, xxx, xxx);
return p;
}
此时等价于
tagTest GetObj();
|
C++之变量相关
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
class CLuoTest
{
public:
CLuoTest();
~CLuoTest();
int IAdd();
void SetVal(int nVal1, int nVal2);
private:
int m_nVal1;
int m_nVal2;
};
CLuoTest::CLuoTest()
{
m_nVal1 = 10;
m_nVal2 = 20;
};
CLuoTest::~CLuoTest()
{
printf("CLuoTest::~CLuoTest\r\n");
};
int CLuoTest::IAdd()
{
return m_nVal1 + m_nVal2;
};
void CLuoTest::SetVal(int nVal1, int nVal2)
{
m_nVal1 = nVal1;
m_nVal2 = nVal2;
}
|
类对象为局部变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest LuoTest;
LuoTest.SetVal(1, 2);
int nSum = LuoTest.IAdd();
printf("%d\r\n", nSum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
识别成员函数
Release
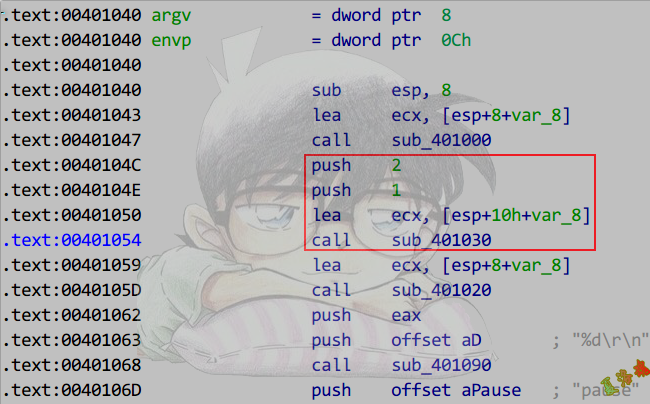
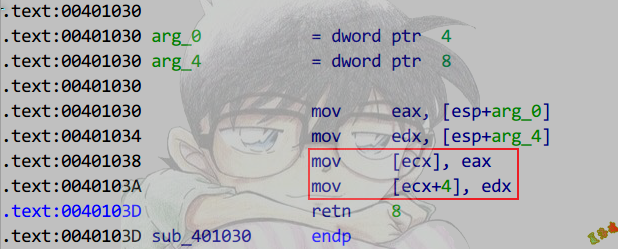
特征
1
2
3
|
①第一参数为this指针,默认使用ecx传参.
②函数内对第一参数this指针做间接访问.
注意:如果成员函数为_cdecl或_stdcall调用约定,this指针通过栈传送且为第一参数.
|
识别构造函数
Release
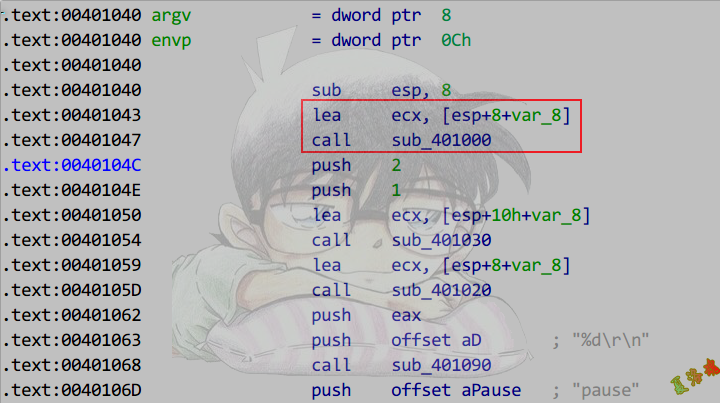
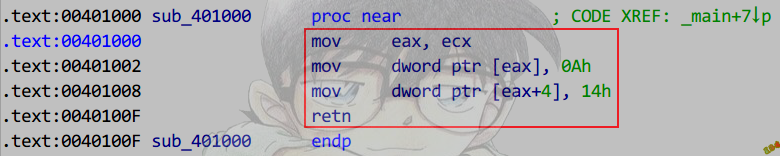
特征
1
2
3
4
|
必要条件:
①必为thiscall调用约定.
②构造函数是该对象进入作用域后的第一次成员函数调用.
③返回this指针.
|
识别析构函数
Release
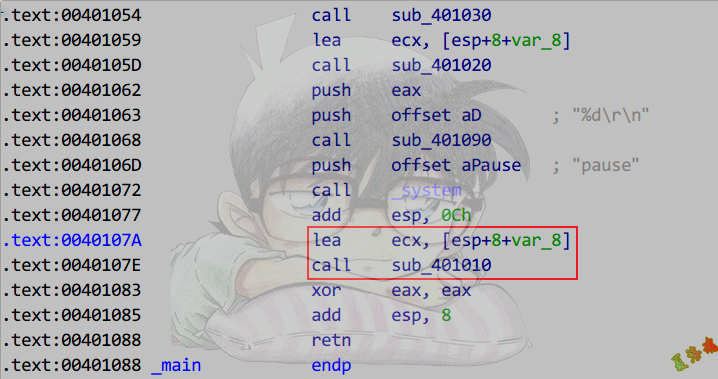
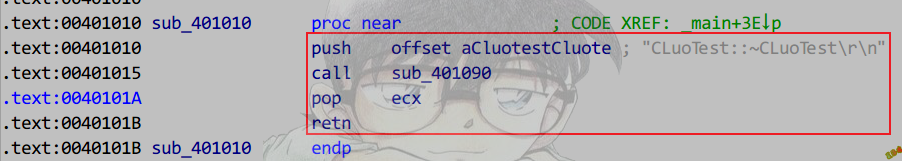
特征
1
2
3
4
|
必要条件:
①必为thiscall调用约定.
②析构函数是该对象进入作用域后的最后一次成员函数调用.
③无返回值定义.
|
类对象为全局变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
CLuoTest g_LuoTest;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
g_LuoTest.SetVal(1, 2);
int nSum = g_LuoTest.IAdd();
printf("%d\r\n", nSum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
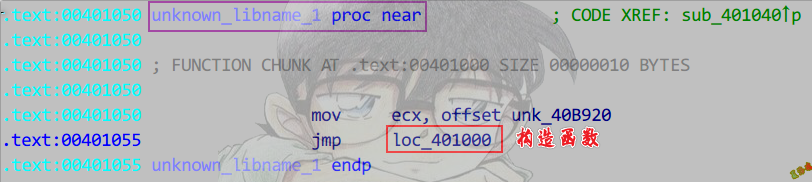
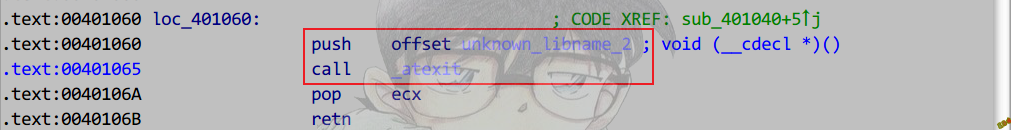
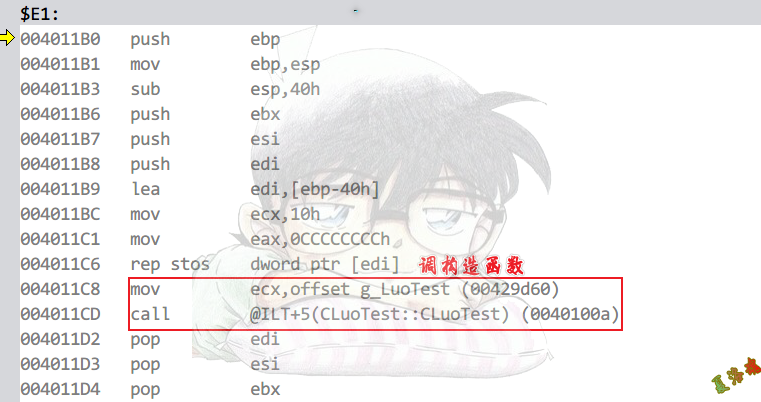
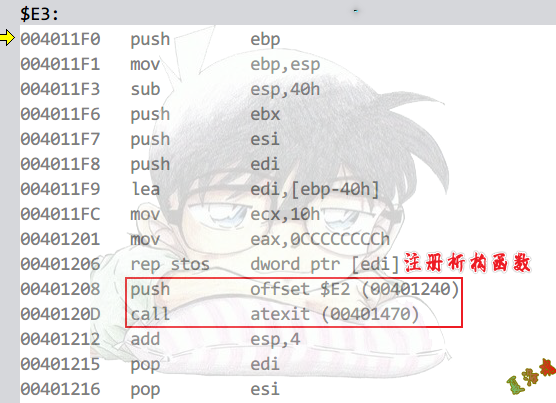
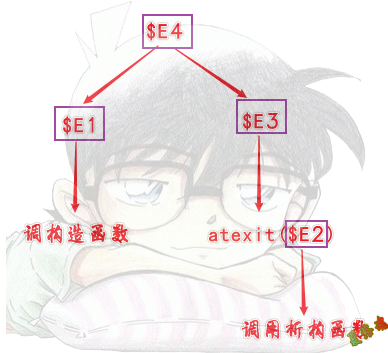
构造函数和析构函数:
在__cinit函数的第二个__initterm函数中调用.
Release
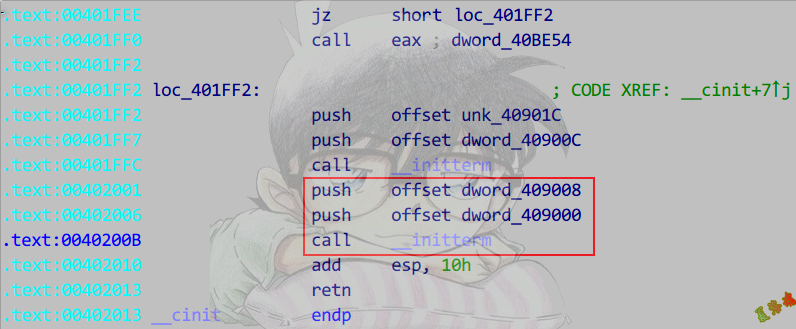
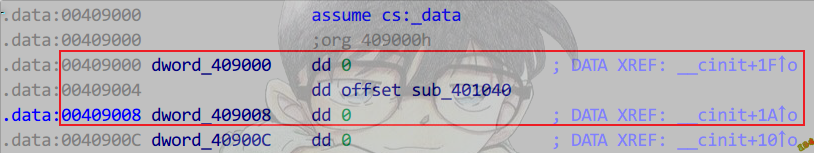
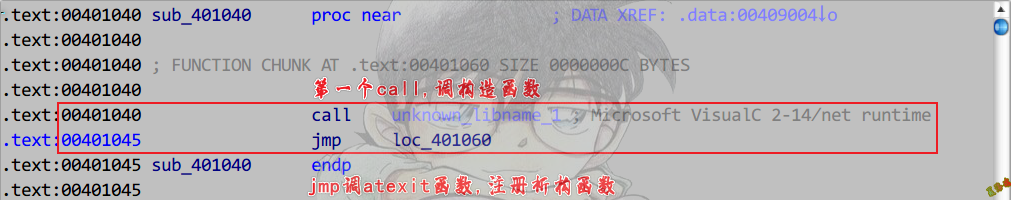
Main函数执行完,会执行atexit注册的函数.
构造函数
析构函数
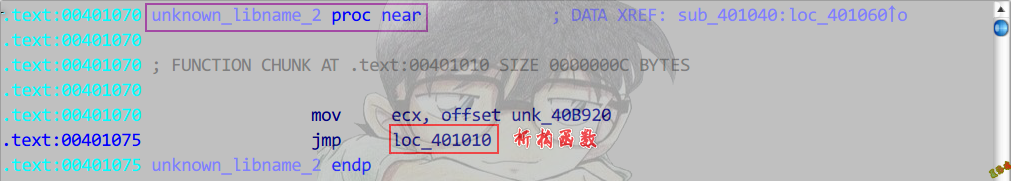
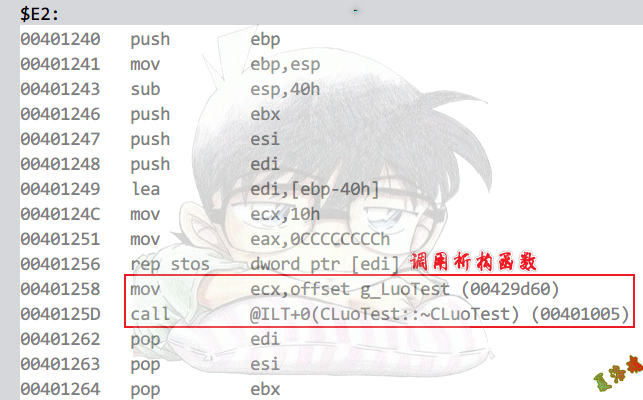
Debug
在__initterm的函数指针调用.
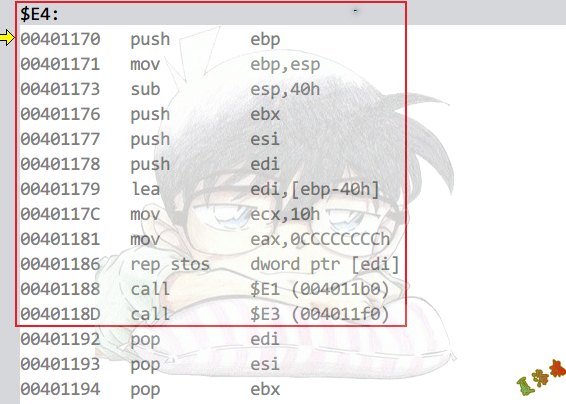
构造函数
析构函数
总结
类对象为堆变量
New单个对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest* pLuoTest = new CLuoTest;
pLuoTest->SetVal(1, 2);
int nSum = pLuoTest->IAdd();
printf("%d\r\n", nSum);
delete pLuoTest;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Release
new
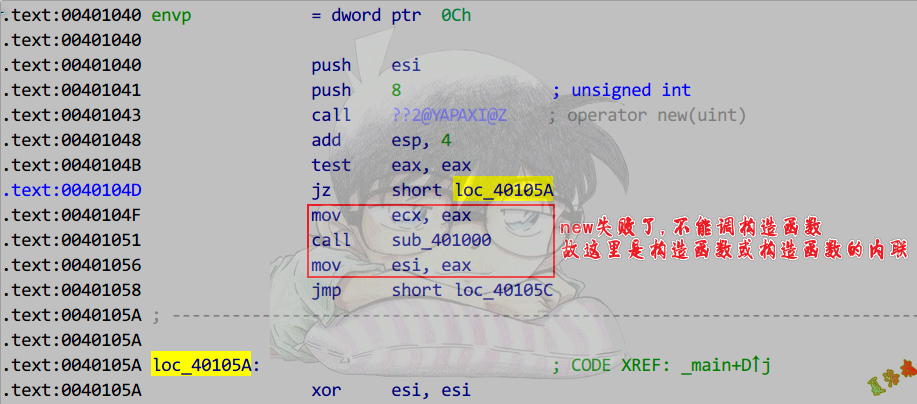
delete
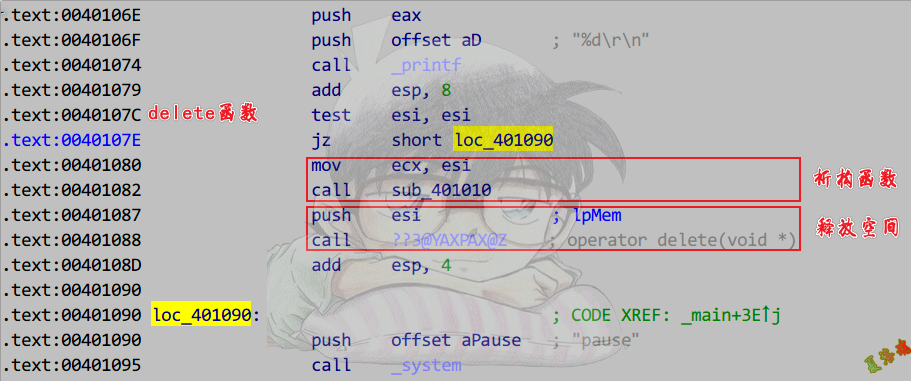
注意
1
2
3
4
|
new和delete函数会自动检查指针是否为空.
但我们仍然需要自己检查指针是否为空.
因为编译器做的检查,是为了是否执行构造函数或析构函数.
而我们做的检查,是为了让我们在别的地方使用这个指针的时候,指针不为空.
|
Debug
new
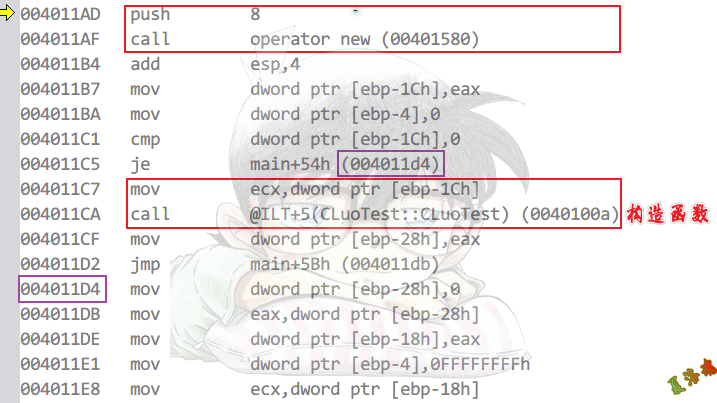
delete
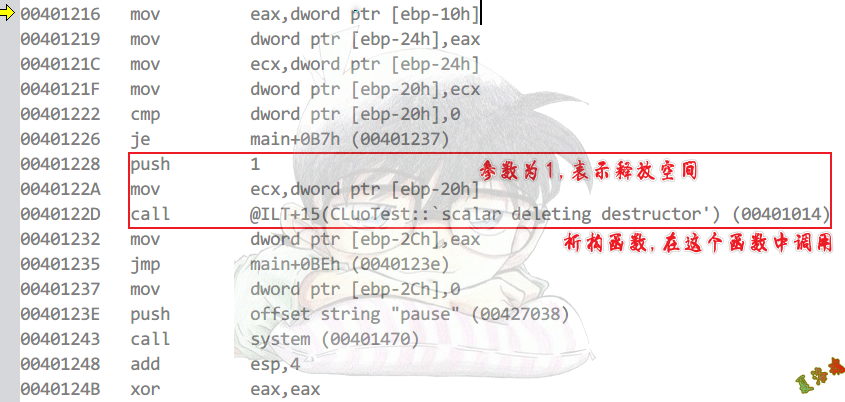
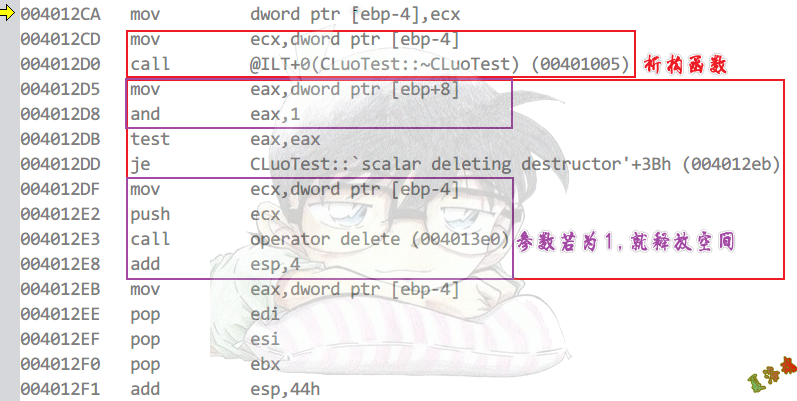
之所以会出现上述代码,是因为我们有可能写出如下代码.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest* pLuoTest = new CLuoTest;
pLuoTest->SetVal(1, 2);
int nSum = pLuoTest->IAdd();
printf("%d\r\n", nSum);
pLuoTest->~CLuoTest(); //人工调析构,反复利用同一个空间
pLuoTest->CLuoTest::CLuoTest();
pLuoTest->SetVal(10, 20);
nSum = pLuoTest->IAdd();
printf("%d\r\n", nSum);
delete pLuoTest;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
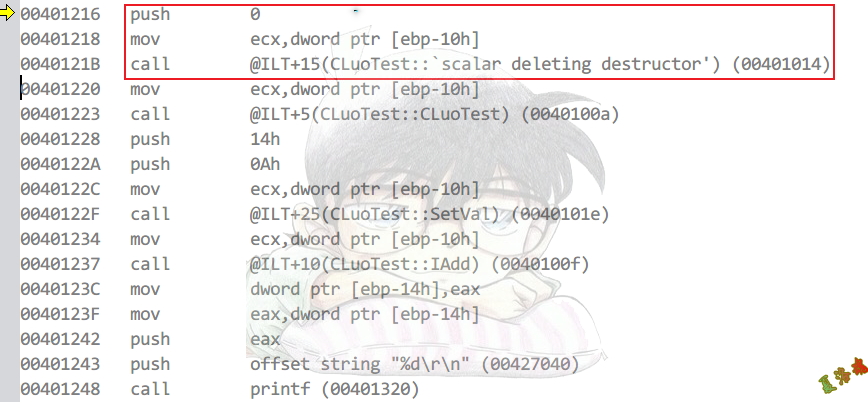
此时push的参数就会是0,只执行析构函数,不释放空间.
New对象数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest* pLuoTest = new CLuoTest[5];
pLuoTest->SetVal(1, 2);
int nSum = pLuoTest->IAdd();
printf("%d\r\n", nSum);
delete[] pLuoTest;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
new
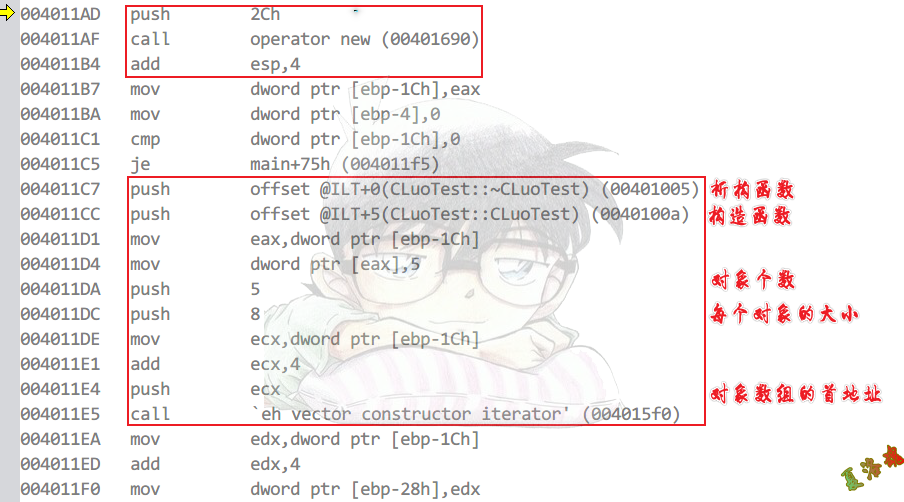
这个地方需要析构函数是因为,遇到new失败时,虽然前面的new成功,,但也算整个new对象数组的失败,需要把前面成功new的对象析构掉.
detete[]
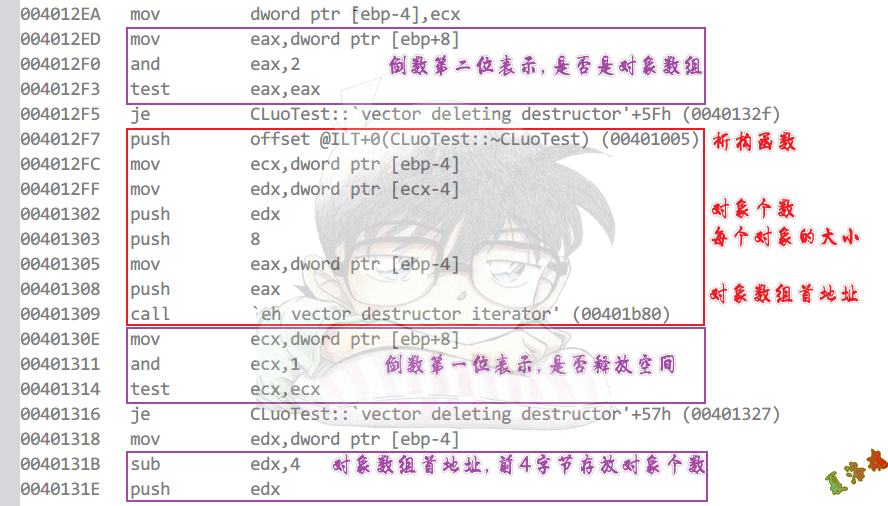
C++之对象相关
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
class CLuoTest
{
public:
CLuoTest();
~CLuoTest();
void Show();
void SetVal(int nVal1, int nVal2);
private:
int m_nVal1;
int m_nVal2;
char m_szName[20];
};
CLuoTest::CLuoTest()
{
m_nVal1 = 10;
m_nVal2 = 20;
strcpy(m_szName, "Luo");
printf("CLuoTest::CLuoTest\r\n");
};
CLuoTest::~CLuoTest()
{
printf("CLuoTest::~CLuoTest\r\n");
};
void CLuoTest::Show()
{
printf("%d, %d, %s\r\n", m_nVal1, m_nVal2, m_szName);
};
void CLuoTest::SetVal(int nVal1, int nVal2)
{
m_nVal1 = nVal1;
m_nVal2 = nVal2;
strcpy(m_szName, "Hun");
}
|
对象传参
1
2
3
4
|
void foo(CLuoTest LuoTest)
{
LuoTest.Show();
}
|
无拷贝构造
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest LuoTest;
LuoTest.SetVal(10, 20);
foo(LuoTest);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Release
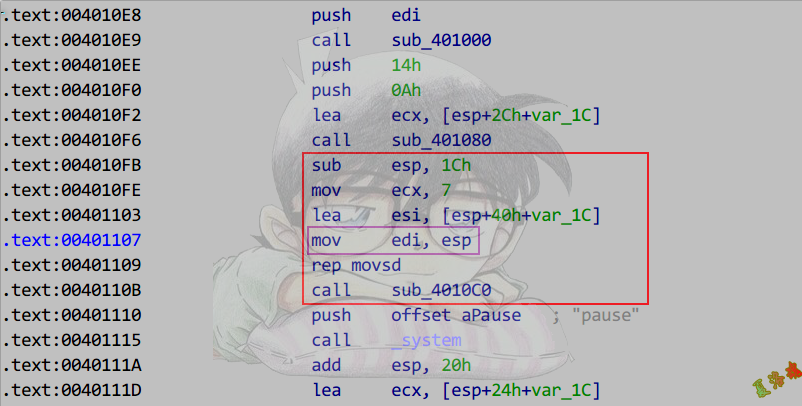
特征
1
|
以栈顶为Dst,对象地址为Src,执行memcpy,浅拷贝.
|
有拷贝构造
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/*
//拷贝构造
CLuoTest::CLuoTest(CLuoTest& Obj)
{
m_nVal1 = Obj.m_nVal1;
m_nVal2 = Obj. m_nVal2;
strncpy(m_szName, Obj. m_szName, 20);
}
*/
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest LuoTest;
LuoTest.SetVal(10, 20);
foo(LuoTest);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
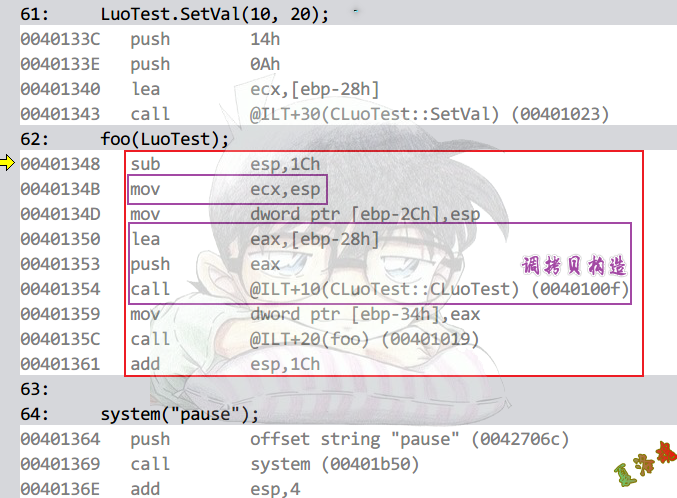
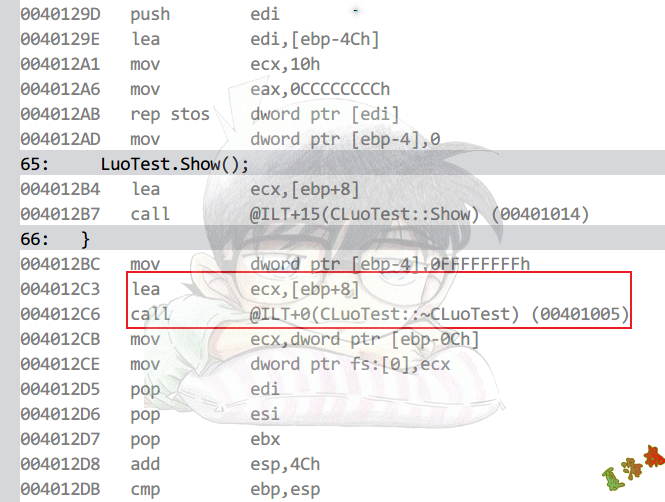
Release
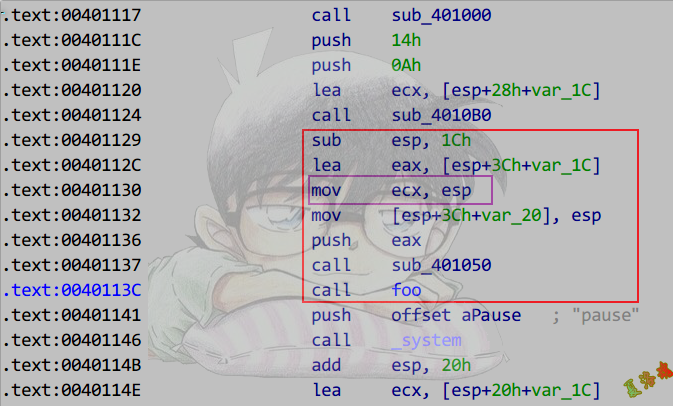
特征
1
2
3
|
①将栈顶作为this指针给ecx,调用拷贝构造
关键语句:mov ecx, esp
②函数外调用构造函数,函数内调用析构函数
|
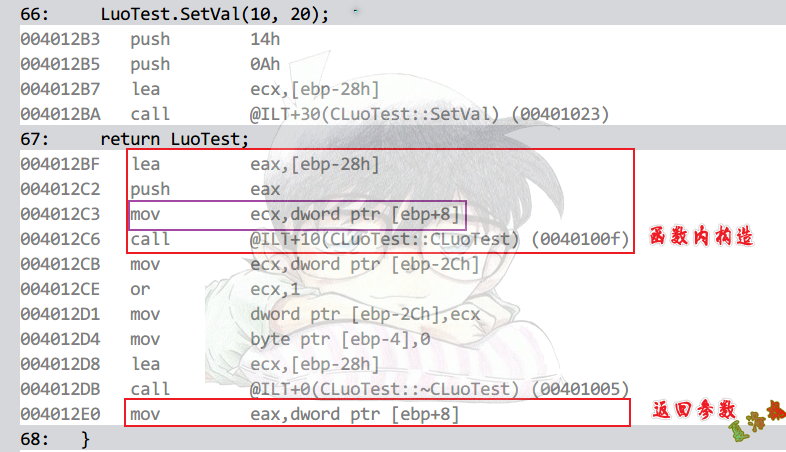
对象返回
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
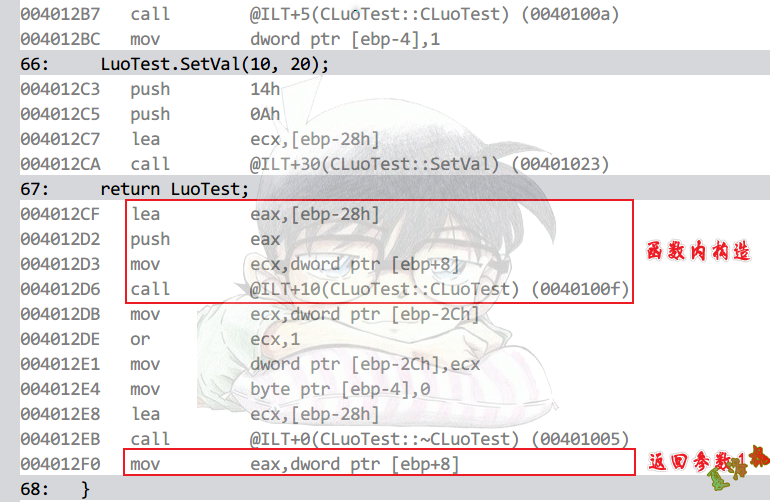
CLuoTest GetObj()
{
CLuoTest LuoTest;
LuoTest.SetVal(10, 20);
return LuoTest;
}
|
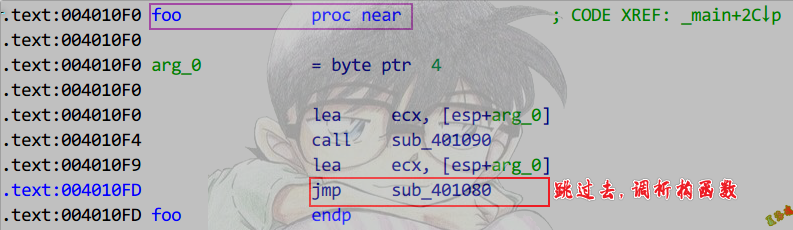
拷贝构造
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
/*
//拷贝构造
CLuoTest::CLuoTest(CLuoTest& obj)
{
m_nVal1 = obj.m_nVal1;
m_nVal2 = obj. m_nVal2;
strncpy(m_szName, obj. m_szName, 20);
}
*/
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest HunTest = GetObj(); //拷贝构造
HunTest.Show();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
浅拷贝
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest HunTest;
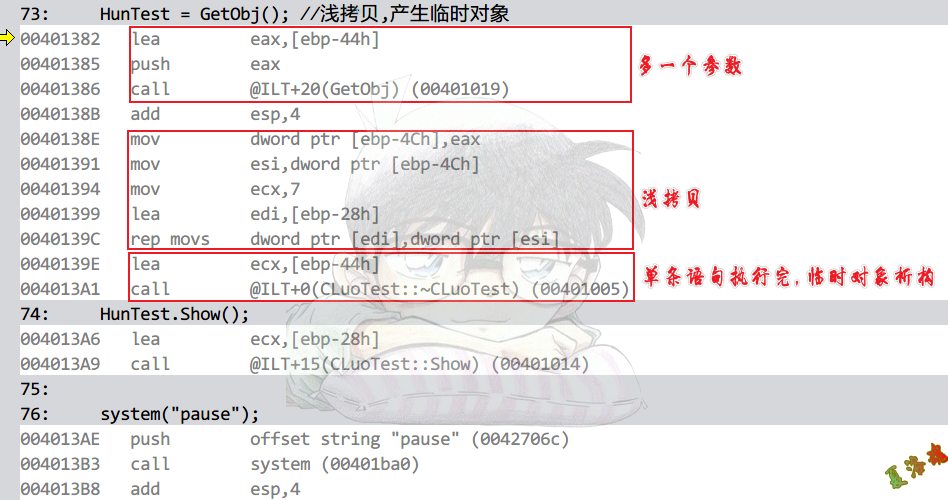
HunTest = GetObj(); //浅拷贝,产生临时对象
HunTest.Show();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
特征
1
2
|
①调用函数结束后,会执行以返回值为Src,目标对象为Dst的memcpy.
②临时对象,即多传进去的那个参数会执行析构.
|
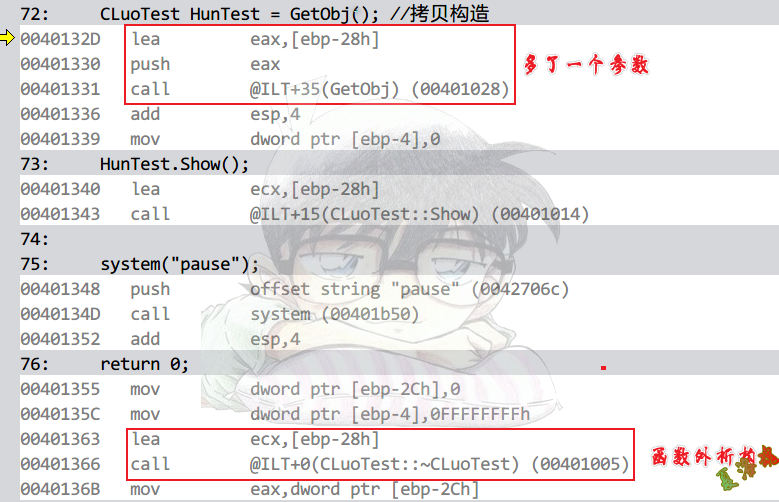
无名对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest& Ref = GetObj(); //产生无名对象,遇到分号不析构,生命周期随Ref
Ref.Show();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
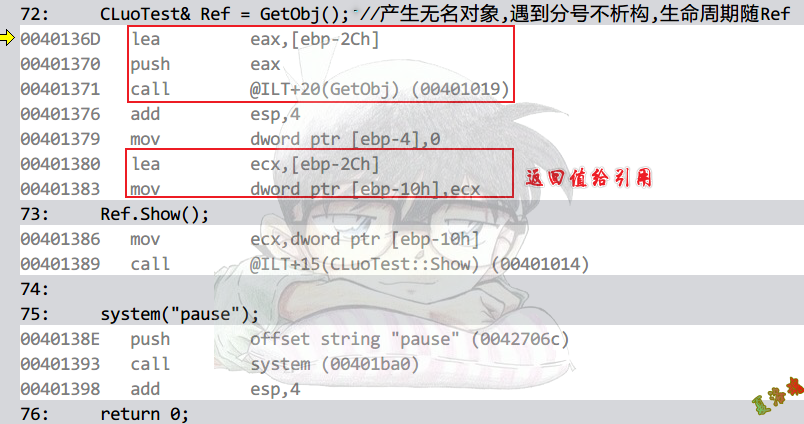
特征
1
2
3
|
①函数多了一个参数.
②函数内构造,函数外析构.
③返回参数1.
|
运算符重载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
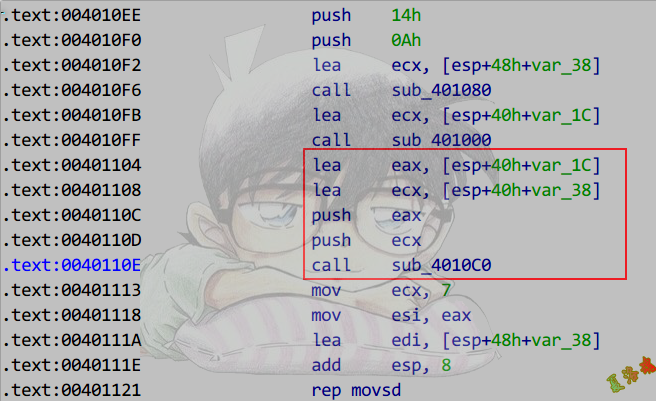
/*
//运算符重载
//类内声明为友元函数
friend CLuoTest& operator+(CLuoTest& ObjDst, CLuoTest& ObjSrc);
CLuoTest& operator+(CLuoTest& ObjDst, CLuoTest& ObjSrc)
{
ObjDst.m_nVal1 += ObjSrc.m_nVal1;
ObjDst.m_nVal2 += ObjSrc.m_nVal2;
return ObjDst;
}
*/
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest LuoTest;
LuoTest.SetVal(10, 20);
CLuoTest HunTest;
LuoTest = LuoTest + HunTest; //中缀式,实际调用方式为波兰式 LuoTest = operator+(LuoTest, HunTest);
LuoTest.Show();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Release
静态局部
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
static CLuoTest LuoTest;
LuoTest.Show();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Release
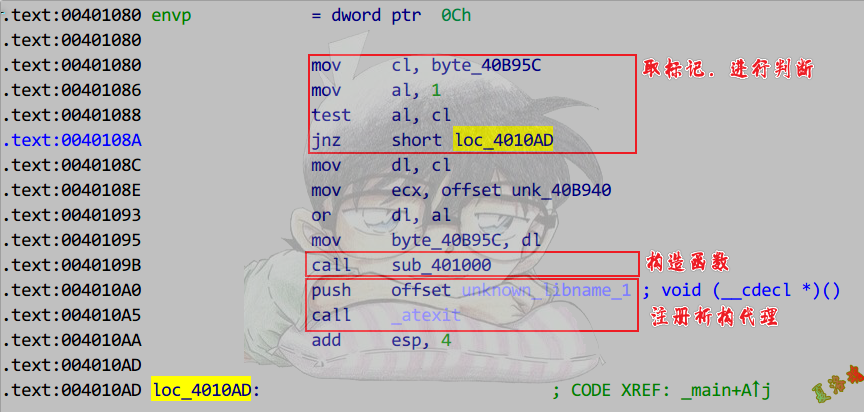
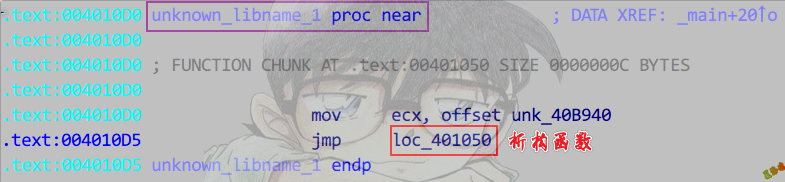
特征
1
2
|
①用一个标记来记录静态局部对象是否已初始化.
②若未初始化,则执行构造函数,并注册析构代理.
|
C++之单重继承
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
class CLuoTest
{
public:
CLuoTest();
CLuoTest::CLuoTest(CLuoTest& Obj);
virtual ~CLuoTest();
virtual void Show();
void SetVal(int nVal1, int nVal2);
private:
int m_nVal1;
int m_nVal2;
char m_szName[20];
};
CLuoTest::CLuoTest()
{
m_nVal1 = 10;
m_nVal2 = 20;
strcpy(m_szName, "Luo");
printf("CLuoTest::CLuoTest\r\n");
};
CLuoTest::CLuoTest(CLuoTest& Obj)
{
m_nVal1 = Obj.m_nVal1;
m_nVal2 = Obj.m_nVal2;
strncpy(m_szName, Obj.m_szName, 20);
}
CLuoTest::~CLuoTest()
{
printf("CLuoTest::~CLuoTest\r\n");
};
void CLuoTest::Show()
{
printf("CLuoTest:%d, %d, %s\r\n", m_nVal1, m_nVal2, m_szName);
};
void CLuoTest::SetVal(int nVal1, int nVal2)
{
m_nVal1 = nVal1;
m_nVal2 = nVal2;
strcpy(m_szName, "Hun");
}
|
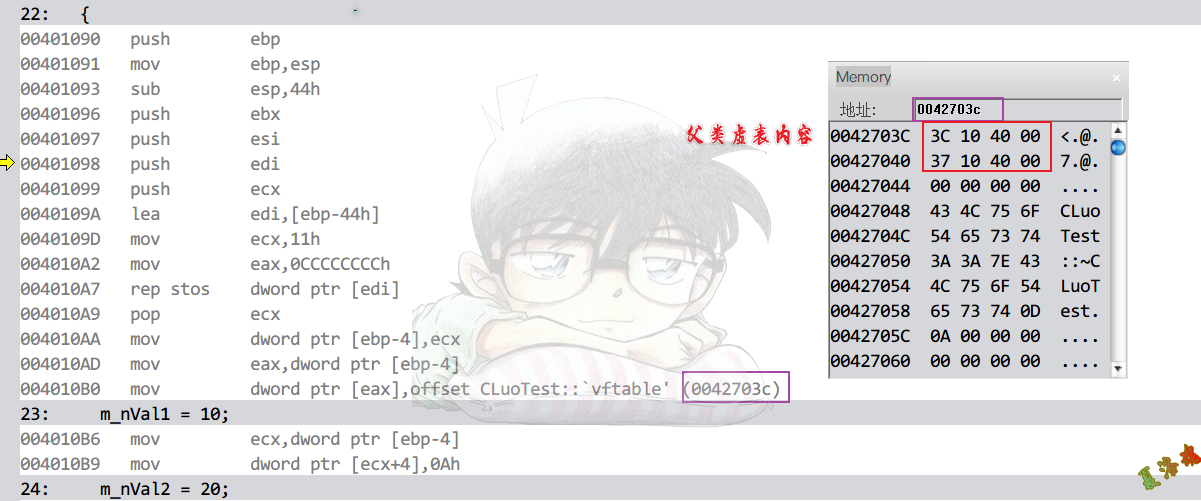
虚函数
只有使用对象的指针或引用调用虚函数时,才有访问虚表,间接调用的动作.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest LuoObj;
LuoObj.Show();
CLuoTest& HunObj = LuoObj;
HunObj.Show();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
调用方式
Debug
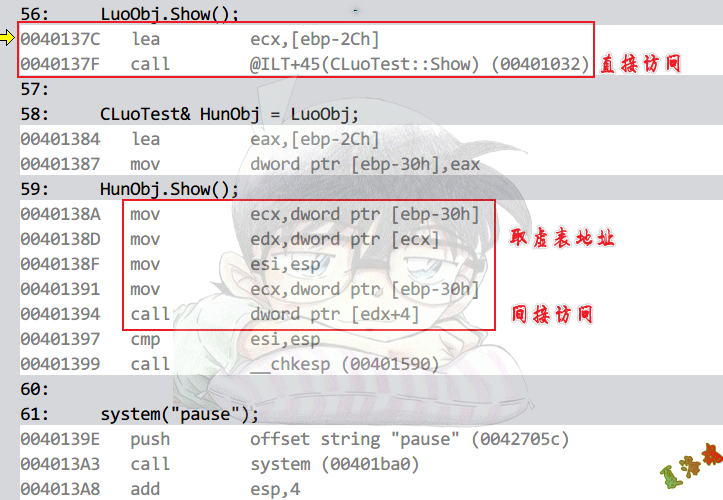
特征
构造函数
Debug
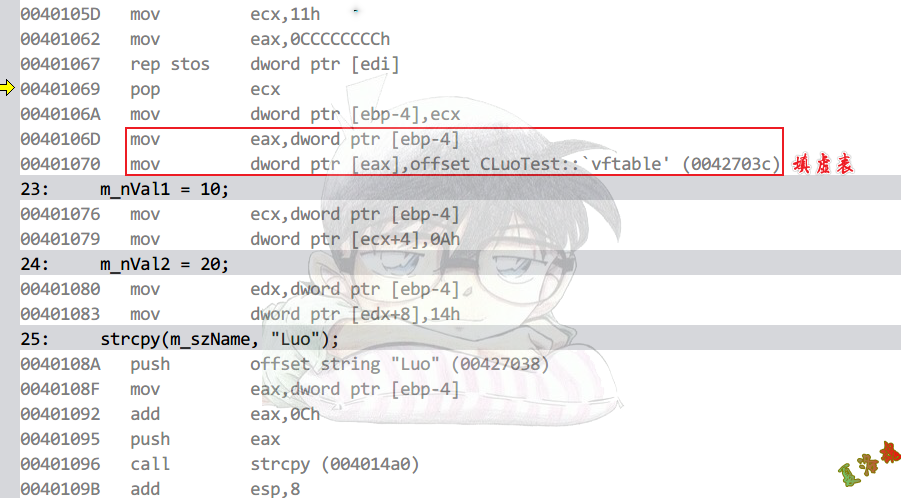
特征
1
2
|
构造函数会填写虚表,这个地址在只读数据区.
注意:虚表中的函数指针不是0结尾,需通过实际调用,来判断虚函数.
|
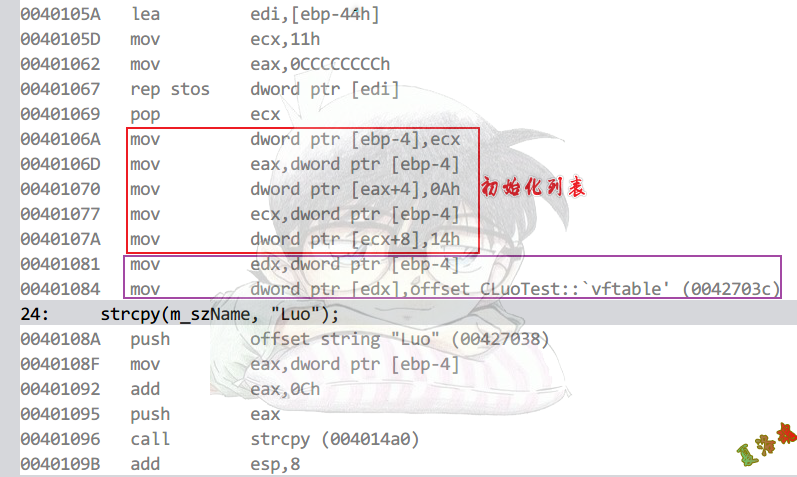
初始化列表
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
CLuoTest::CLuoTest()
:m_nVal1(10), m_nVal2(20)
{
strcpy(m_szName, "Luo");
printf("CLuoTest::CLuoTest\r\n");
}
|
Debug
析构函数
Debug
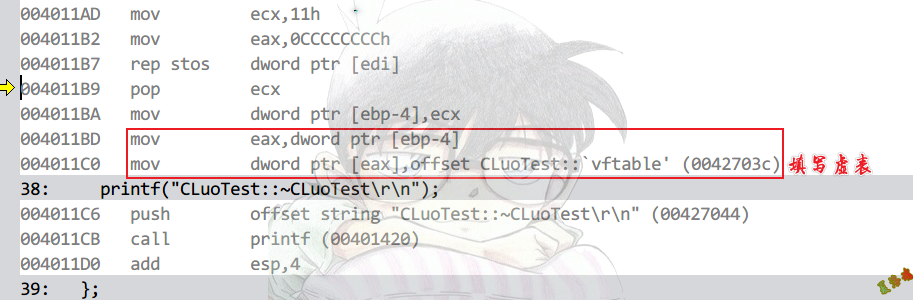
特征
注意
为什么析构函数会填写虚表?
假设有类A和类B.
B继承A,构造时填写的是B的虚表.
而当B析构完,还需要析构A,但此时this指针中的虚表填写的是B的虚表.
如果此时我们通过虚表间接访问,就会访问到B的函数,但是B已经析构完了.
故需要在析构的时候回填虚表.
单重继承有虚函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
class CHunTest : public CLuoTest
{
public:
CHunTest();
virtual ~CHunTest();
virtual void Show();
private:
int m_nVal1;
int m_nVal2;
char m_szName[20];
};
CHunTest::CHunTest()
{
m_nVal1 = 100;
m_nVal2 = 200;
strcpy(m_szName, "Hun");
printf("CHunTest::CHunTest\r\n");
}
CHunTest::~CHunTest()
{
printf("CHunTest::~CHunTest\r\n");
}
void CHunTest::Show()
{
printf("CHunTest:%d, %d, %s\r\n", m_nVal1, m_nVal2, m_szName);
}
|
构造函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest* pLuoObj = new CHunTest;
pLuoObj->Show();
delete pLuoObj;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
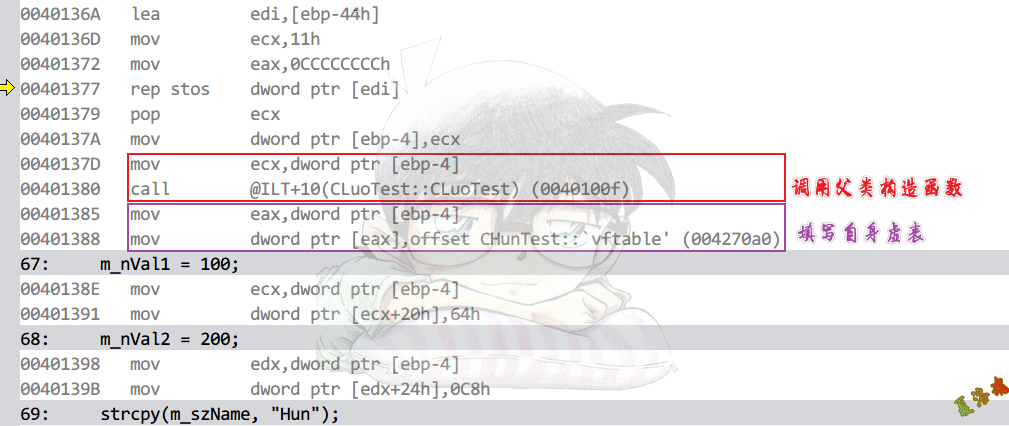
虚表内容
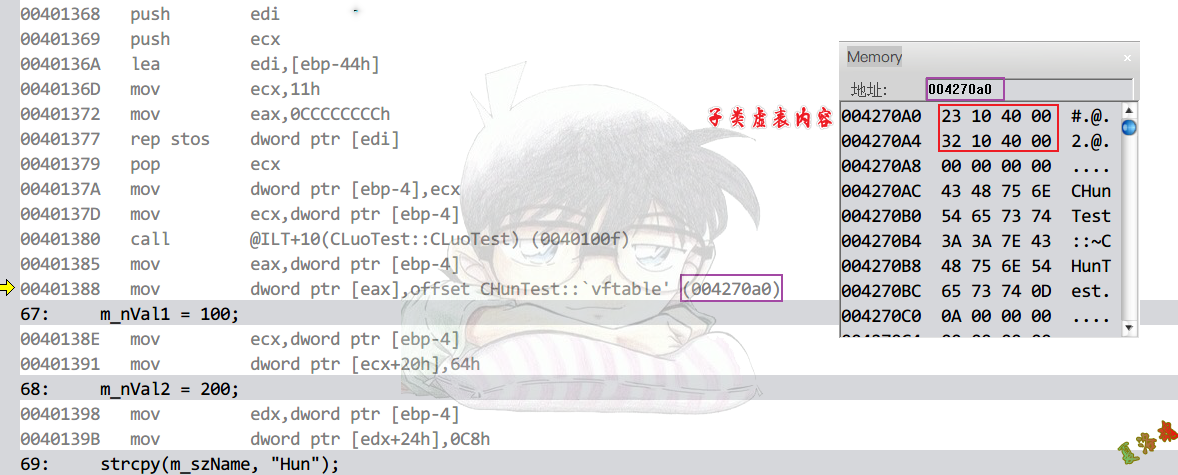
技巧之交叉引用
- 查看虚表引用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoTest* pLuoObj = new CHunTest;
pLuoObj->Show();
delete pLuoObj;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
- 找到构造函数,识别出虚表地址
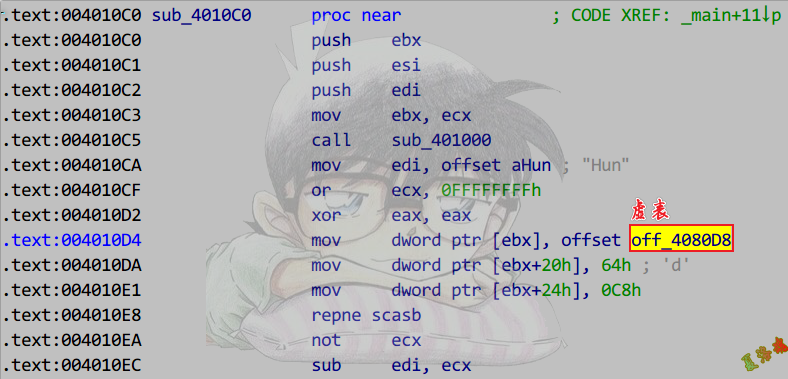
- 右键Xrefs graph to
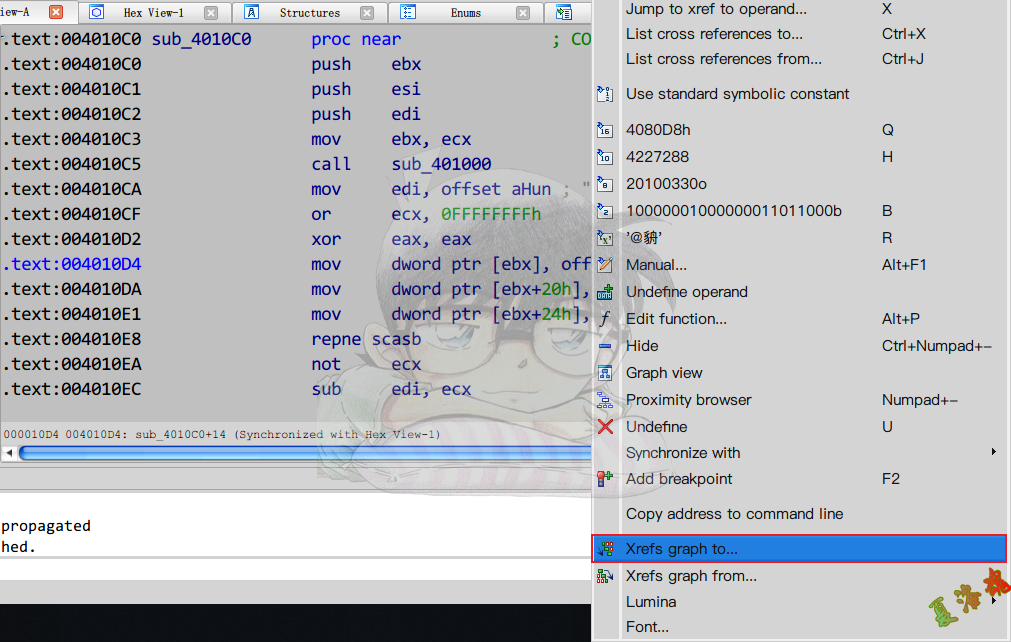
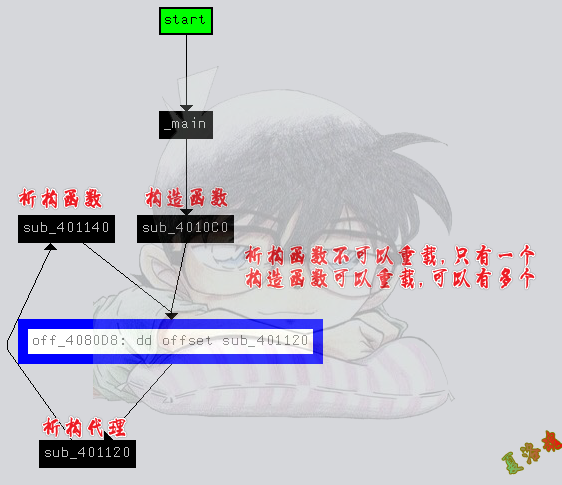
从这张图中,我们就可以知道构造函数和析构函数.
- 查看构造函数引用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
CHunTest g_HunObj;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CHunTest HunObj1;
CHunTest HunObj2;
CHunTest HunObj3;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
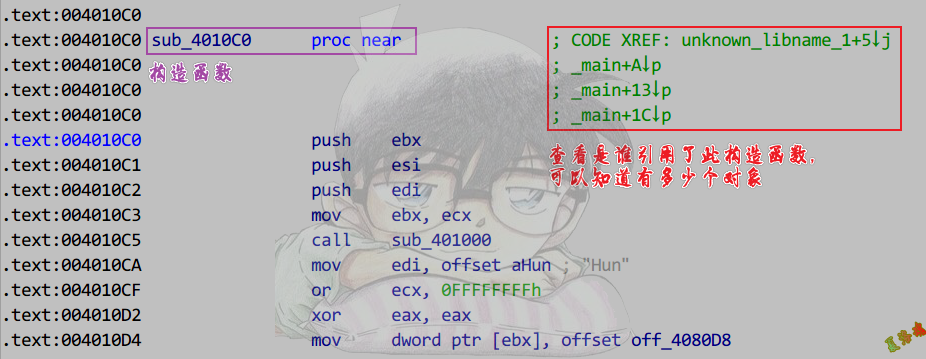
- 查看父类构造函数引用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
class CHunTest1 : public CLuoTest
{
};
class CHunTest2 : public CLuoTest
{
};
class CHunTest3 : public CLuoTest
{
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CHunTest HunObj;
CHunTest1 HunObj1;
CHunTest2 HunObj2;
CHunTest3 HunObj3;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
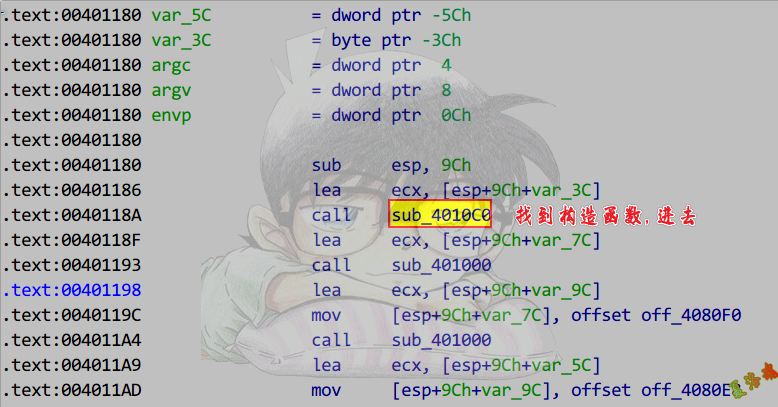
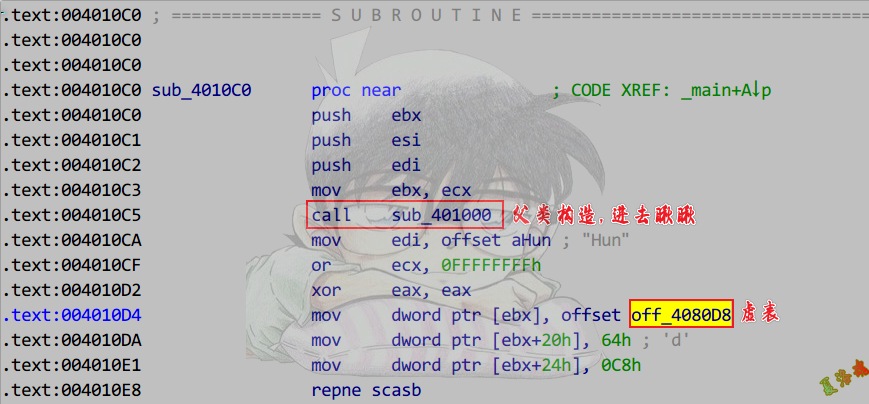
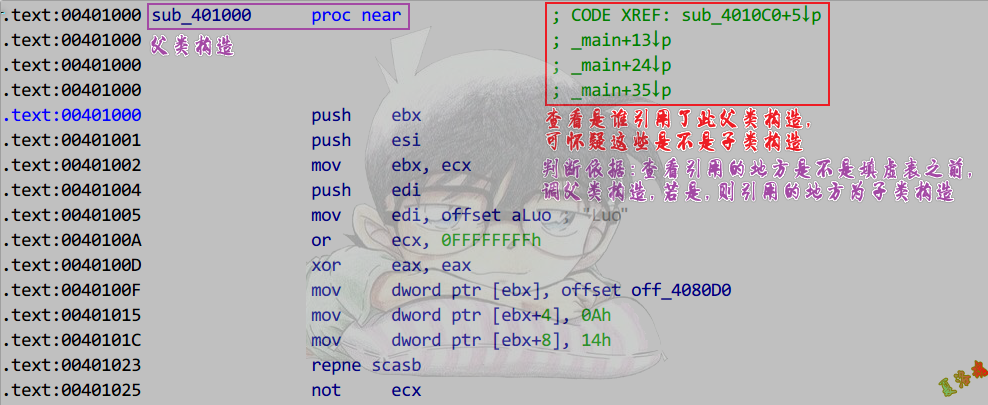
C++之对象关系
继承:
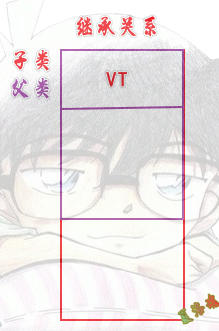
特征
包含:
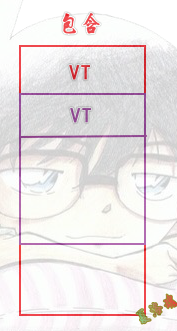
特征
1
2
|
不共用虚表,同一虚表位置写一次.
当红色对象析构时,紫色对象也不在了.
|
聚合:
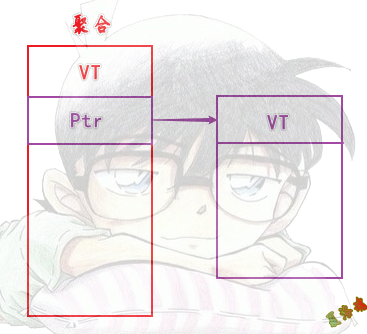
特征
注意
当无虚表时,继承和包含无法区分.
因为面向对象,是通过行为区分的,不是通过数据区分的.
虚表用来区分每个对象是什么.
数据用来区分同类型实体的差异.
C++之多重继承
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
class CLuoTest
{
public:
CLuoTest();
virtual ~CLuoTest();
virtual void Show();
private:
int m_nVal1;
int m_nVal2;
char m_szName[20];
};
CLuoTest::CLuoTest()
{
m_nVal1 = 10;
m_nVal2 = 20;
strcpy(m_szName, "Luo");
printf("CLuoTest::CLuoTest\r\n");
};
CLuoTest::~CLuoTest()
{
printf("CLuoTest::~CLuoTest\r\n");
};
void CLuoTest::Show()
{
printf("CLuoTest:%d, %d, %s\r\n", m_nVal1, m_nVal2, m_szName);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
class CHunTest
{
public:
CHunTest();
virtual ~CHunTest();
virtual void Show();
private:
int m_nVal1;
int m_nVal2;
char m_szName[20];
};
CHunTest::CHunTest()
{
m_nVal1 = 100;
m_nVal2 = 200;
strcpy(m_szName, "Hun");
printf("CHunTest::CHunTest\r\n");
}
CHunTest::~CHunTest()
{
printf("CHunTest::~CHunTest\r\n");
}
void CHunTest::Show()
{
printf("CHunTest:%d, %d, %s\r\n", m_nVal1, m_nVal2, m_szName);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
class CLuoHunTest : public CLuoTest, public CHunTest
{
public:
CLuoHunTest();
virtual ~CLuoHunTest();
virtual void Show();
private:
int m_nVal1;
int m_nVal2;
char m_szName[20];
};
CLuoHunTest::CLuoHunTest()
{
m_nVal1 = 1000;
m_nVal2 = 2000;
strcpy(m_szName, "LuoHun");
printf("CLuoHunTest::CLuoHunTest\r\n");
}
CLuoHunTest::~CLuoHunTest()
{
printf("CLuoHunTest::~CLuoHunTest\r\n");
}
void CLuoHunTest::Show()
{
printf("CLuoHunTest:%d, %d, %s\r\n", m_nVal1, m_nVal2, m_szName);
}
|
内存模型:
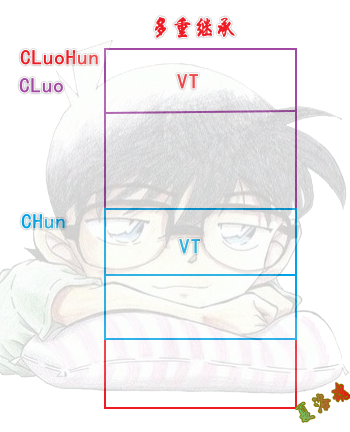
CLuo和CHun的顺序,按继承时的书写顺序,从左到右.
构造函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoHunTest* pObj = new CLuoHunTest;
pObj->Show();
delete pObj;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
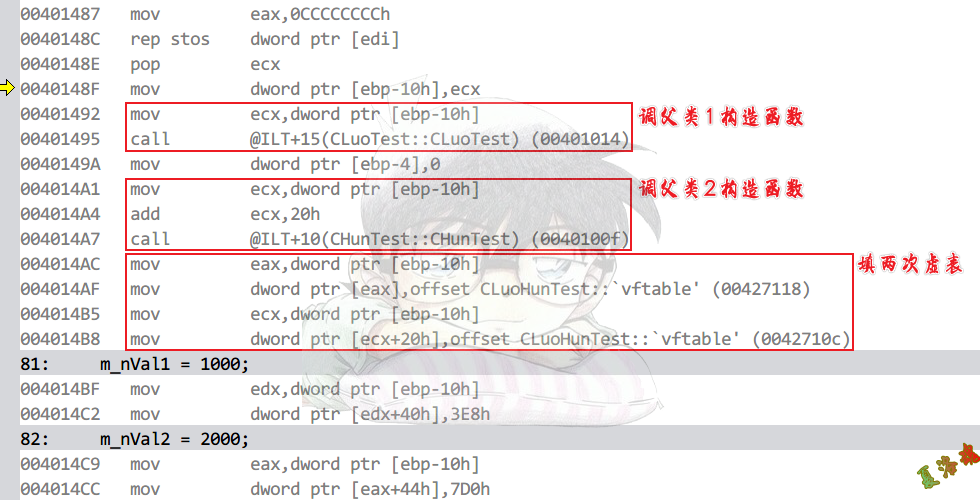
特征
1
|
先调父类构造,然后有几个父类,就填写几次虚表.
|
同类型指针转换:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoHunTest LuoHunObj;
CLuoTest* pLuoObj = &LuoHunObj;
CHunTest* pHunObj = &LuoHunObj; //这个地方会产生一个分支
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
Debug
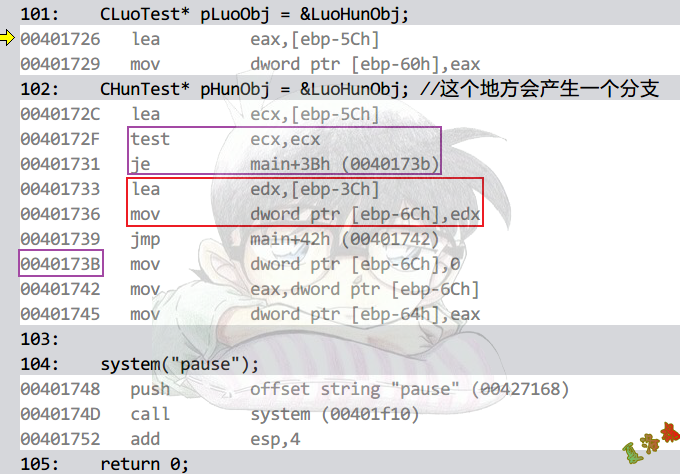
注意
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
为什么会产生一个分支?
CLuoHunTest LuoHunObj;
CLuoTest* pLuoObj = &LuoHunObj;
CHunTest* pHunObj = &LuoHunObj;//这个地方会移动This指针,假如说&LuoHunObj +0x10位置是CHunTest对象的位置,当&LuoHunObj 不为NULL时,这样是正确的,但如果&LuoHunObj为NULL,即下列代码,若无脑+0x10,结果就是错误的了
CLuoTest* pLuoObj = NULL;
CHunTest* pHunObj = NULL;
|
纯虚函数识别:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
class CLuoTest
{
public:
CLuoTest();
virtual ~CLuoTest();
virtual void Show() = 0;
};
CLuoTest::CLuoTest()
{
};
CLuoTest::~CLuoTest()
{
printf("CLuoTest::~CLuoTest\r\n");
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
class CLuoHunTest : public CLuoTest
{
public:
CLuoHunTest();
virtual ~CLuoHunTest();
virtual void Show();
private:
int m_nVal1;
int m_nVal2;
char m_szName[20];
};
CLuoHunTest::CLuoHunTest()
{
m_nVal1 = 1000;
m_nVal2 = 2000;
strcpy(m_szName, "LuoHun");
printf("CLuoHunTest::CLuoHunTest\r\n");
}
CLuoHunTest::~CLuoHunTest()
{
printf("CLuoHunTest::~CLuoHunTest\r\n");
}
void CLuoHunTest::Show()
{
printf("CLuoHunTest:%d, %d, %s\r\n", m_nVal1, m_nVal2, m_szName);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLuoHunTest LuoHunObj;
LuoHunObj.Show();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
定位到父类虚表的第二项,纯虚函数项
Debug
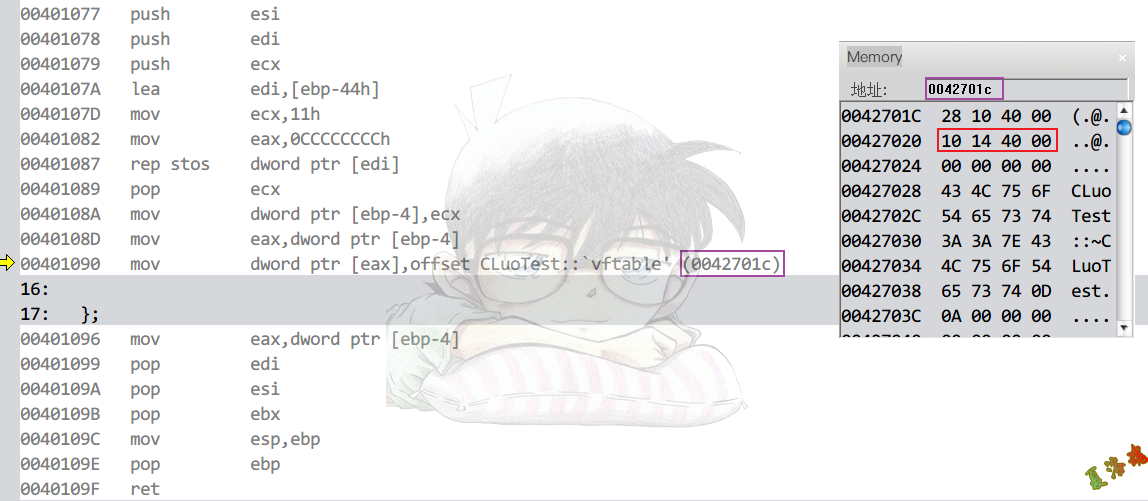
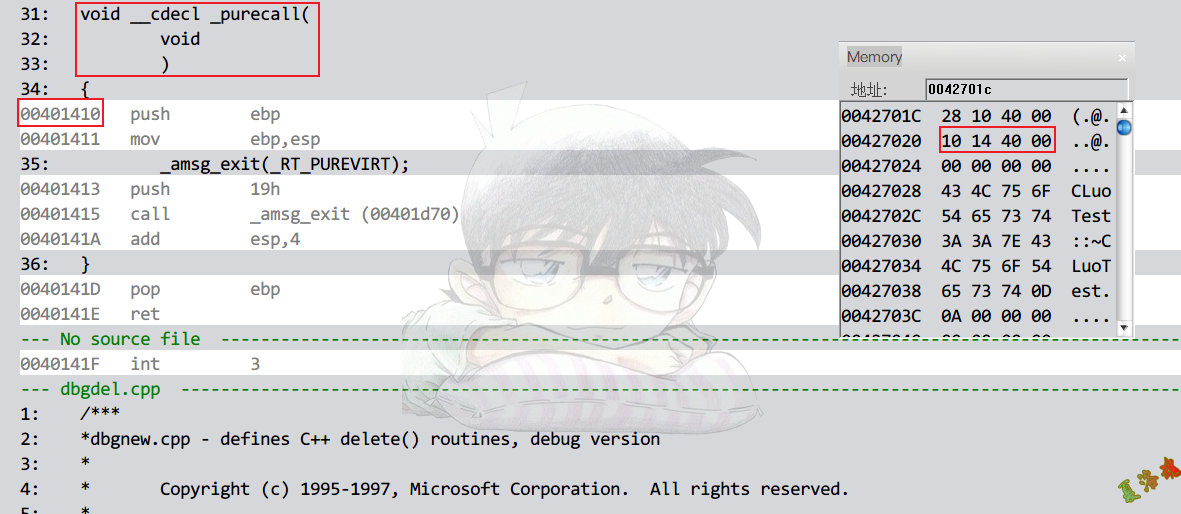
特征
1
2
|
若强制调用纯虚函数,会出现一个错误.
因为虚表中,纯虚函数项填了一个提示错误信息,并关闭的函数指针即_purecall的函数指针.
|
注意
在构造函数或析构函数中调虚函数,不会触发多态.
因为构造函数或析构函数中会回填虚表,填自身对象的虚表地址.
C++之菱形结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
class CLuoA
{
public:
virtual void TestA() {}
virtual void TestCoverA() {}
private:
int m_nValA = 0xAAAAAAAA;
};
class CLuoB : virtual public CLuoA
{
public:
virtual void TestCoverA() {}
virtual void TestB() {}
private:
int m_nValB = 0xBBBBBBBB;
};
class CLuoD : virtual public CLuoA
{
public:
virtual void TestCoverA() {}
virtual void TestD() {}
private:
int m_nValD = 0xDDDDDDDD;
};
class CLuoE :public CLuoB, public CLuoD
{
public:
virtual void TestCoverA() {}
virtual void TestCoverB() {}
virtual void TestCoverD() {}
virtual void TestE() {}
private:
int m_nValE = 0xEEEEEEEE;
};
|
内存模型:
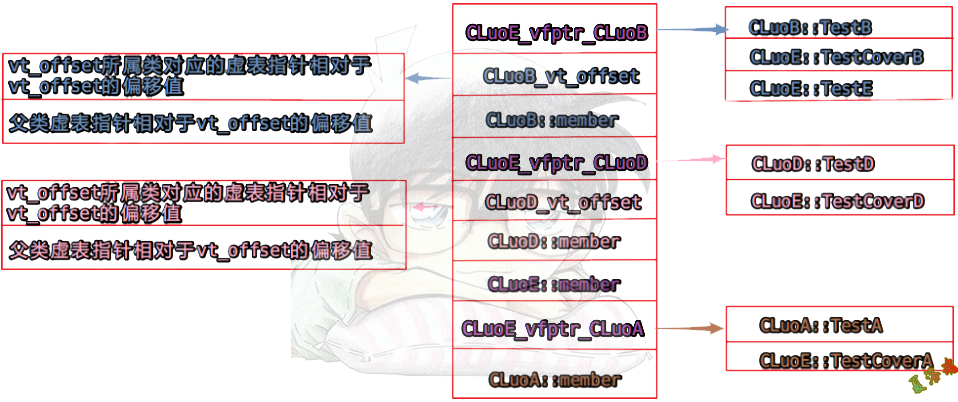
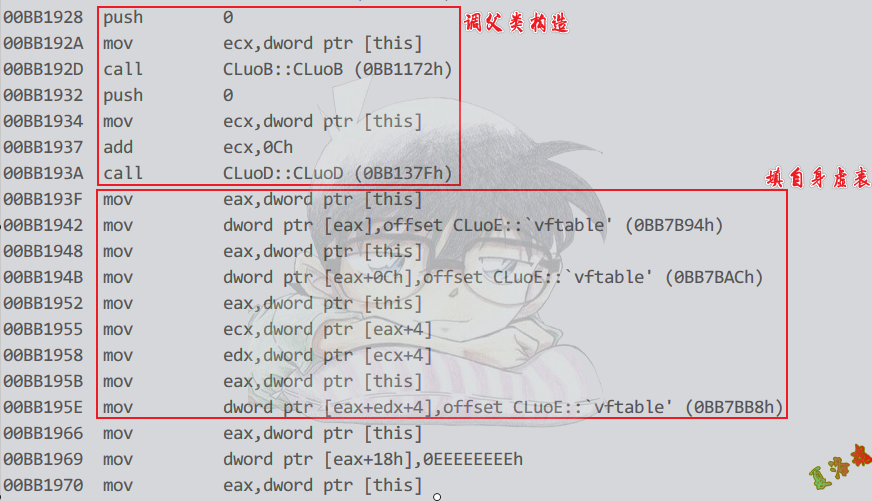
构造函数:
Debug
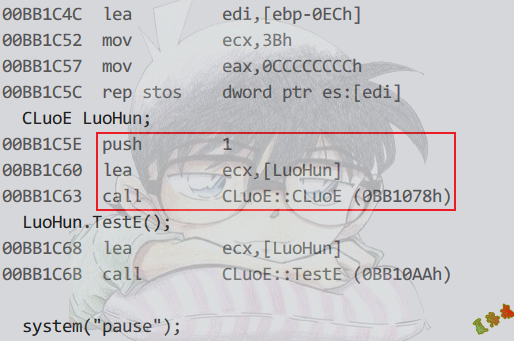
这个地方传1,表明需要填写偏移以及调祖先类构造函数.
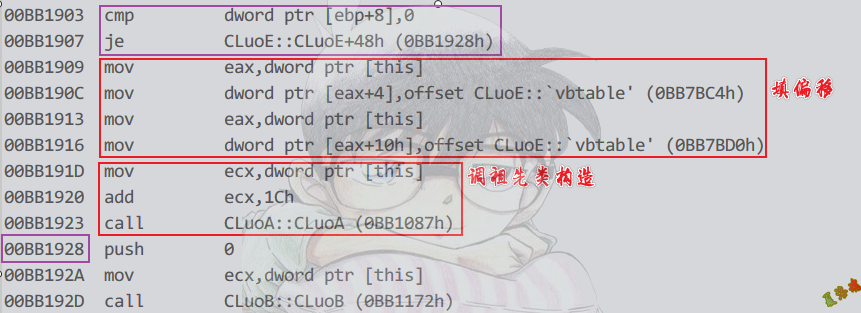
异常
基本数据类型异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void LuoTestException(int n)
{
switch (n)
{
case 0:
{
throw 1;
break;
}
case 1:
{
throw 3.14f;
break;
}
case 2:
{
throw 6.28;
break;
}
case 3:
{
throw 'L';
break;
}
case 4:
{
bool bl = false;
throw bl;
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int nVal = 0;
scanf("%d", &nVal);
try
{
LuoTestException(nVal);
}
catch (int n)
{
printf("catch int %d\r\n", n);
}
catch (float f)
{
printf("catch float %f\r\n", f);
}
catch (double dbl)
{
printf("catch double %lf\r\n", dbl);
}
catch (char ch)
{
printf("catch char %c\r\n", ch);
}
catch (bool b)
{
printf("catch bool %d\r\n", b);
}
catch(...)
{
printf("catch all\r\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
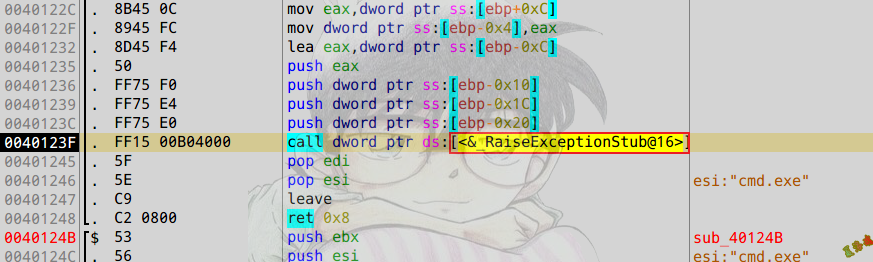
无脑定位异常处理函数
- 如果我们在调试的时候,看到抛异常的函数.
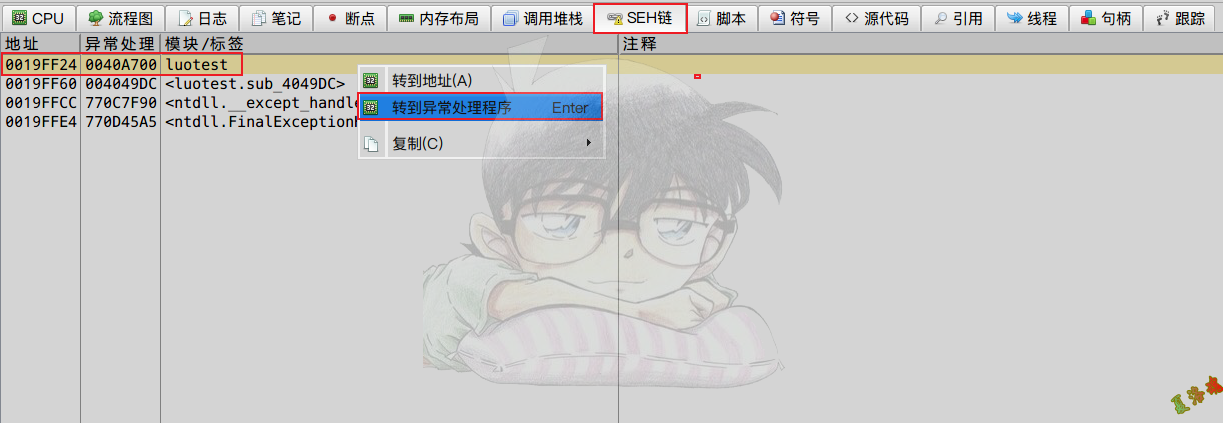
- 我们找到SEH链第一个异常处理的地方,下断,F9运行.
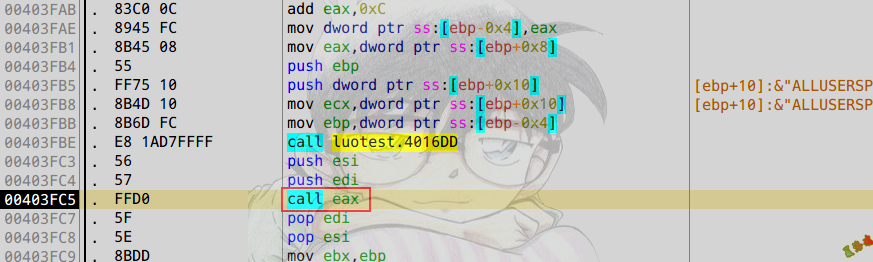
- 按照以下定则进call.
- 找参数最多的call下断点.
- 参数一样,就同时下断,看哪个到达.
- 最后一层是call寄存器(eax).
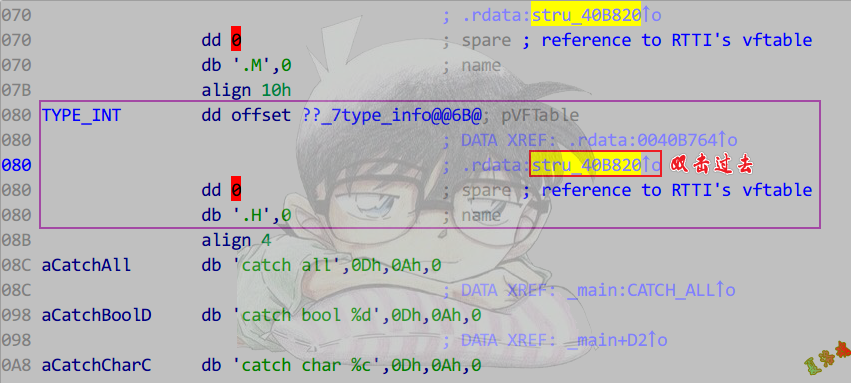
异常信息关系表
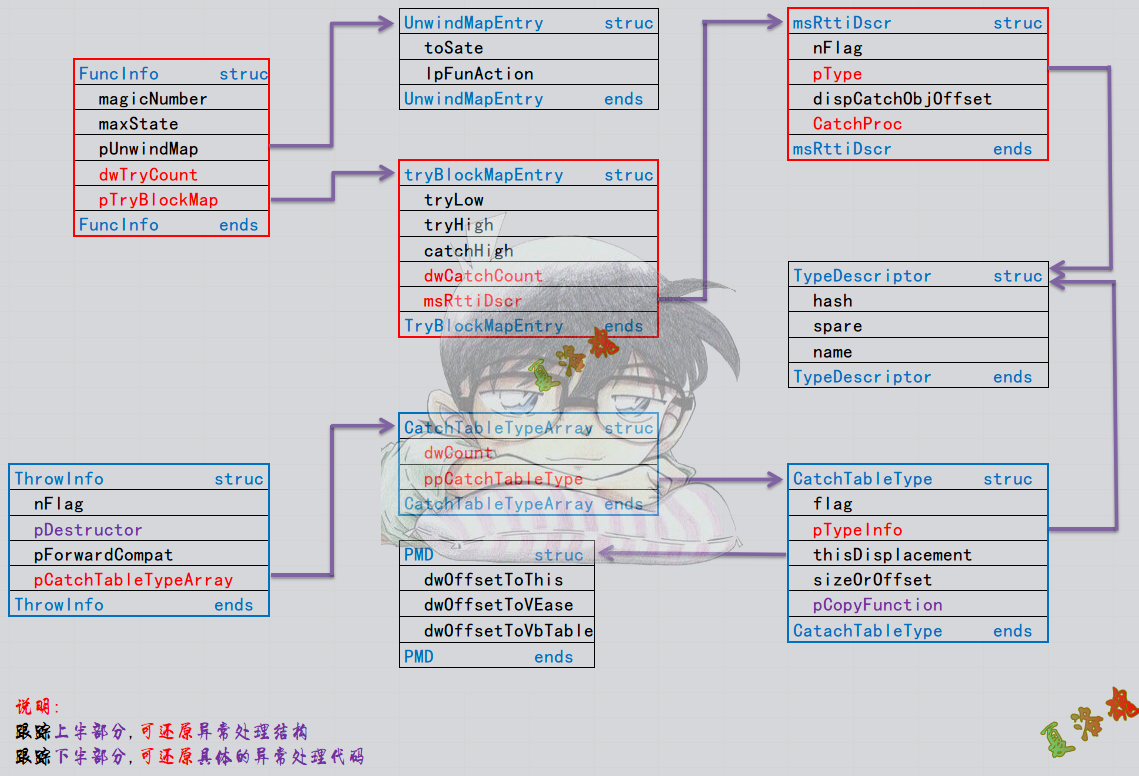
还原异常处理结构(上半部分表)
- 函数开头进入SEH异常链.
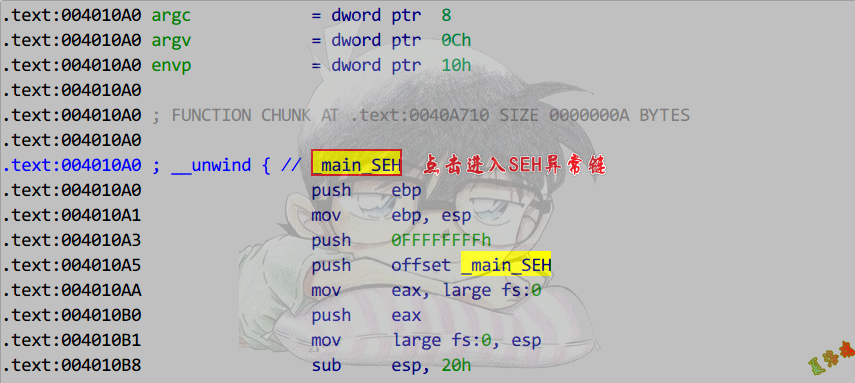
- 找到异常函数信息结构体.
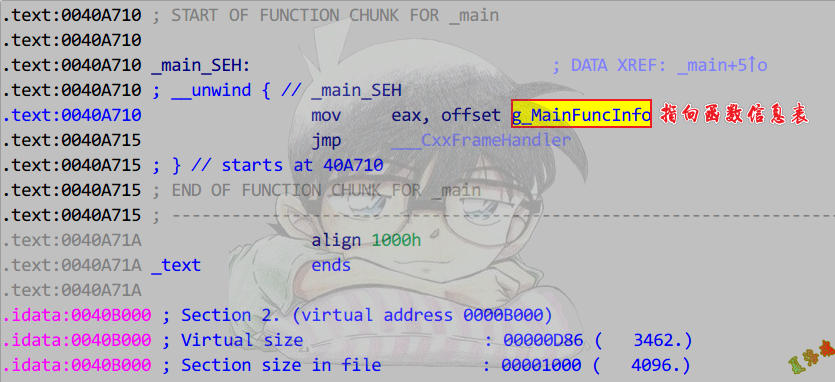
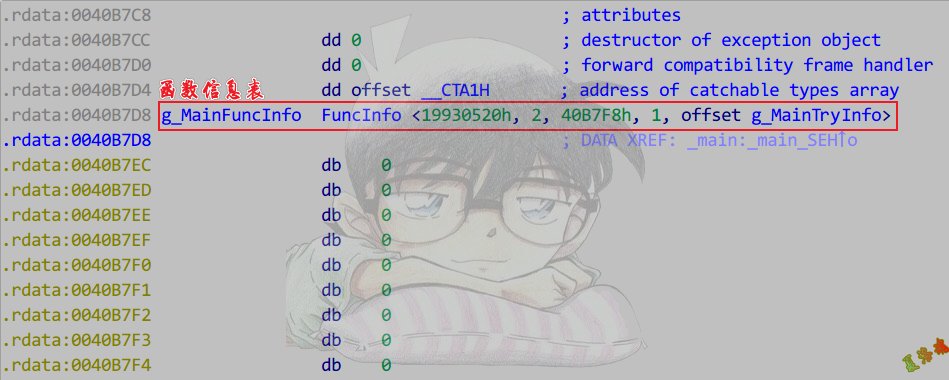
- 分析数据关系.
- 第一张表记录了该函数有几个try,以及对应的try块信息表指针数组.
- 第二张表记录了try对应的catch个数,以及Rtti描述.
- 第三张表记录了catch的类型以及catch的处理函数.
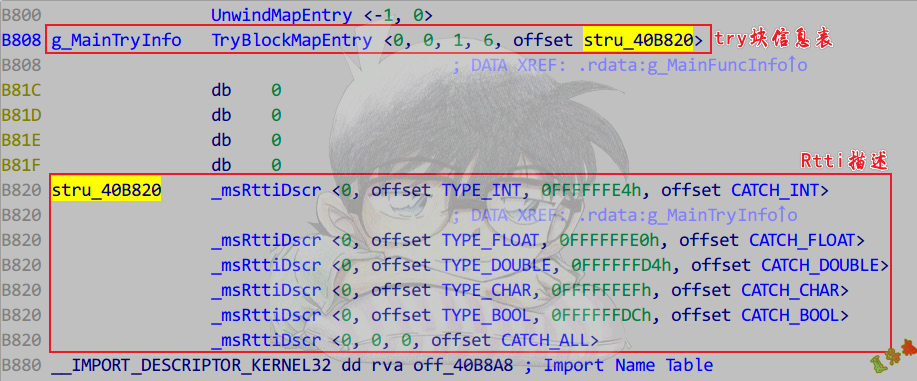
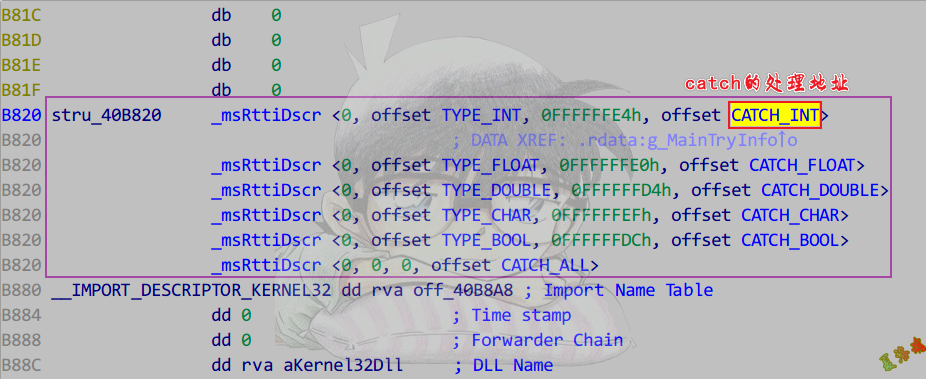
注意:catch的处理函数是有返回值的,返回到catch结束的位置.
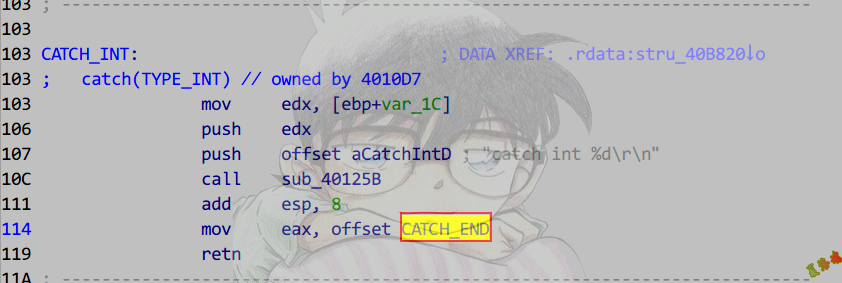
还原具体的异常处理代码(下半部分表)
- 找到函数内抛异常的函数,参数中找抛出的信息表.
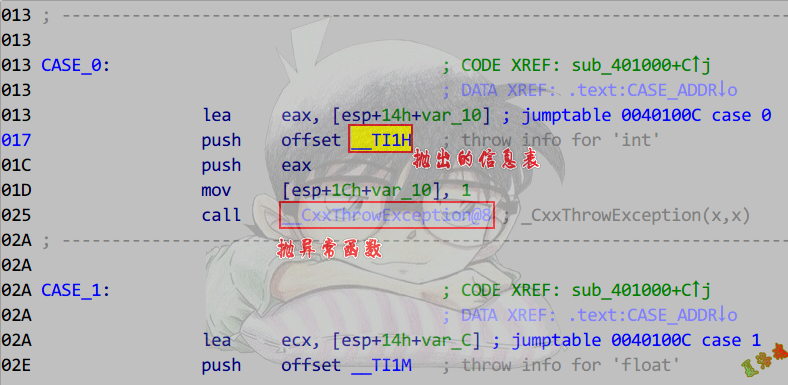
- 找到匹配列表.
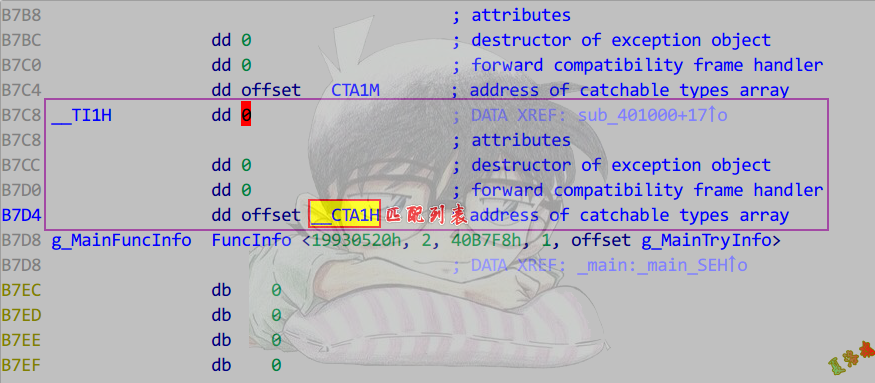
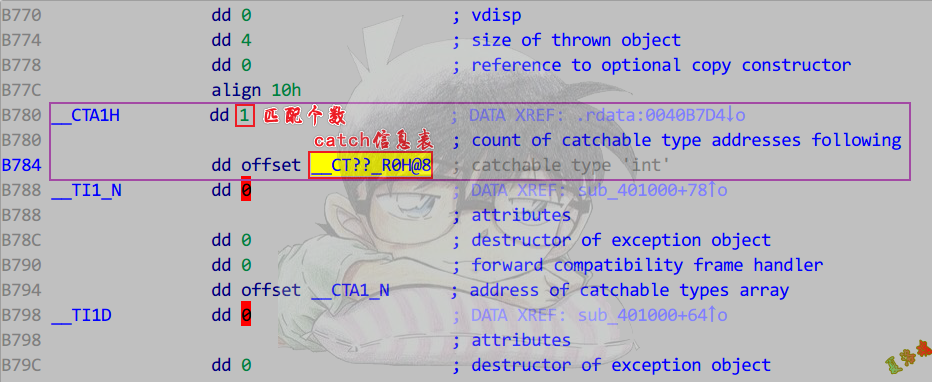
- 在catch信息表中找到类型信息表.
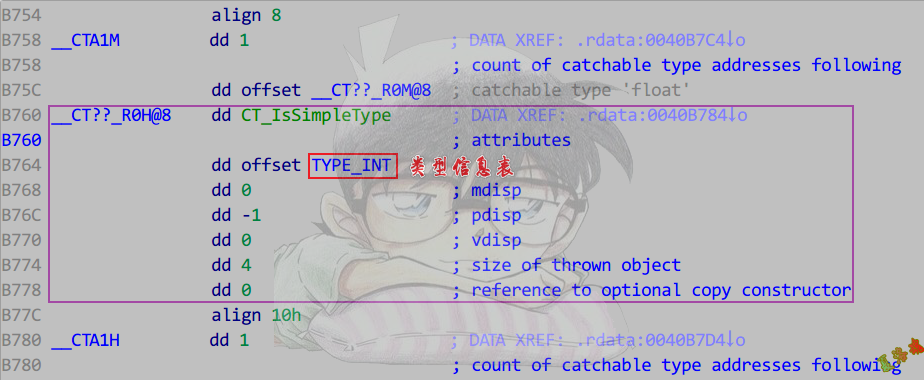
- 对类型信息表,做交叉引用,就可以找到对应的catch处理代码.